The major components of a motorcycle are as follows.
- Body frame
- Engine
- Fuel system
- Transmission
- Electronic system
- Suspension
- Brake
- Wheels
1. BODY FRAME
The motorcycle frame is like a backbone in a human body. A motorcycle frame’s basic aim to provide support to all the parts, like suspensions, engines, and also attached to fuel tank and battery system, etc.
The frame has some hinge points for suspensions and supports the rider or any luggage. All those aerodynamics designs are mostly done on the body frame, that is to reduce those drag and lift force acting on it, and also to increase the down forces, in case of sports bikes. The frame is where all the painting and branding stuffs are done, which gives the bike it’s cool good looking & colorful looks.
Material used in making of the body frame. Earlier, the frames were made of tubular steel only which were very heavy hence reducing the efficiency of the bike. In today’s world, the frames are made of different materials like Aluminium, Steel, Titanium, Magnesium, and Carbon-fibre. The use of these different material plays a very vital role in the cost of the vehicle. Aluminum and Steel are the most commonly used material since they are very cheap compared to others, Whereas Titanium, Carbon-fibre, and Magnesium are used in those bikes which aspire to give sporty and high performance.
2. ENGINE
The motorcycle engine act’s like a heart in a human body. Engine is the most important part of the motorbike. This is the one which brings the motorcycle to life, i,e by giving the power to the system.
It is defined as a machine designed to convert one form of energy into mechanical energy. Here in case of an internal combustion engine that is used in motorcycles, uses fuel (petrol/gasoline, biofuel) to power itself, the reciprocating motion of the piston is transferred to wheels making the motorcycle to move.
Basically, there are two types of an internal combustion engines i,e
- 2-stroke engine
- 4-stroke engine
Two-stroke engine
A two-stroke engine is a type of internal combustion engine which completes a power cycle with two strokes of the piston during only one crankshaft revolution, i,e compression and power stroke.
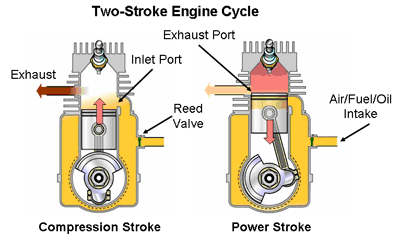
Compression Stroke: when the piston moves downward (to bottom dead center) creating a vacuum inside the cylinder, therefore, the air-fuel mixture is intaken, after which the inlet (reed) valve closes. This is called a compression stroke.
Power Stroke: in power stroke, the piston moves upwards (top dead center) compressing the mixture in the cylinder, after which the spark plug ignites it making the piston move downwards. This is called a power stroke.
Four-stroke engine :
A four-stroke engine is a type of internal combustion engine which completes a power cycle with four strokes of the piston during two crankshaft revolution.
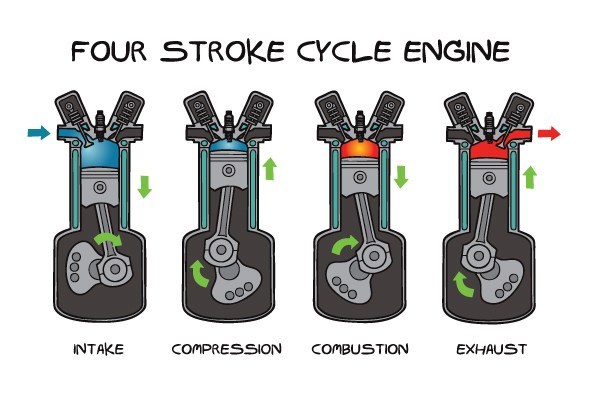
Intake stroke: This is the first stroke. In this stroke, the piston moves downward (to bottom dead center) creating a vacuum inside the cylinder, therefore, the air-fuel mixture is intaken, by opening the inlet valve. This causing the camshaft to make half rotation.
compression stroke: it’s the second stroke, here the intake air-fuel mixture is compressed, thereby increasing its temperature, which makes it burn faster in combustion/power stroke, it causes the camshaft to make half rotation. In this stroke, both the valves remain closed.
Combustion stroke: it’s the third stroke, here the compressed mixture at high-temperature, that is near to its fire point, is ignited with the help of a spark plug, making the piston move upwards. This stroke is done in the second revolution of the camshaft. In this stroke, both the valves remain closed.
Exhaust stroke: it’s the final stroke in the operation, here due to the combustion of the fuel pressure is exerted on the piston thereby moving it down and the exhaust generated is being sent out of the cylinder, by opening the exhaust valve. the second revolution of the camshaft is completed.
3. Fuel system
The fuel is like food to the human body. This is the thing which gives the juice to the engine, to power the system.
Working of a motorcycle fueling system. The fuel is stored in the fuel tank. From which the flow of the fuel is controlled (on/off) by a valve, which is called as “petcock”, and then passed through a pipe to a “carburetor“, which mixes the fuel and air coming from the atmosphere, through an air filter* (filters all dust particles, moisture and other foreign particles). This mixture is called a charge, that develops the power required to run the system.
Carburetor
It is a device used in an internal combustion engine, to mix the air and fuel (air-fuel mixture) in a proper proportion. If there is not enough fuel mixed with the air, the engine “runs lean” and either will not run or damages the engine. If there is too much fuel mixed with the air, the engine “runs rich” and either will not run (it floods), runs poorly or wastes fuel.
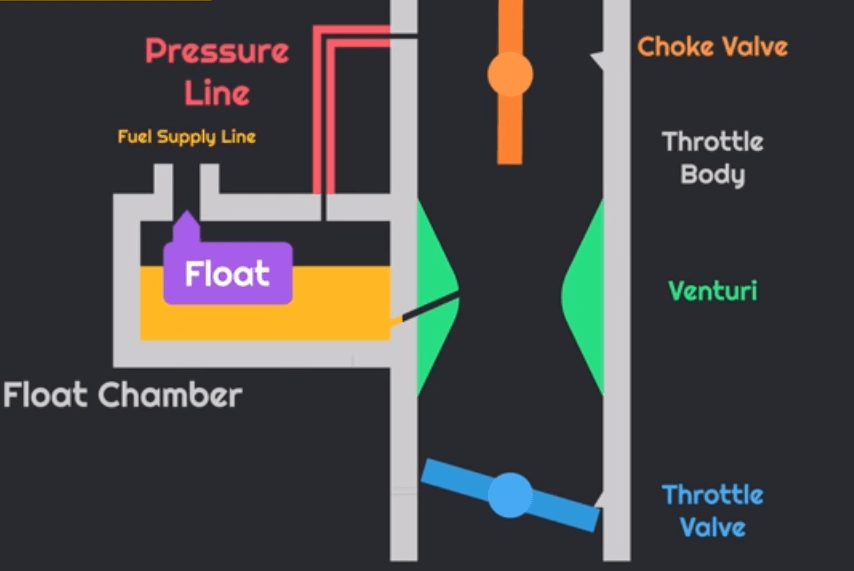
The parts of the carburetor are shown by the above figure. Coming to construction of it, It is provided with a float chamber that collects the fuel from the fuel tank, and it is provided with a pin that regulates the flow of the fuel into the chamber. The two extremes of the carburetor is provided with two valves. The above one is called as choke valve, which regulates the airflow through the system and coming down it is provided with the throttle valve, which regulates the flow of the air-fuel mixture into the engine cylinder. between these valves, a venturi is created to control the velocity of air and fuel
working of carburetor, initially the float chamber is flooded with the fule, and when the accelerator is engaged/passed the throttle valve opens, due to the pressure difference created during the suction stroke, the air through the choke valve enters the chamber and get mixed with the fuel from the float chamber, the venturi regulates the velocity of the fuel and air sent out. now, this mixture is sent into the cylinder through the inlet valve, during the suction stroke.
4. Transmission
Transmission system is which transfers the power developed from engine to the driving parts like wheels etc.
parts in transmission system are
- Gearset
- Clutch
- Transmission drive
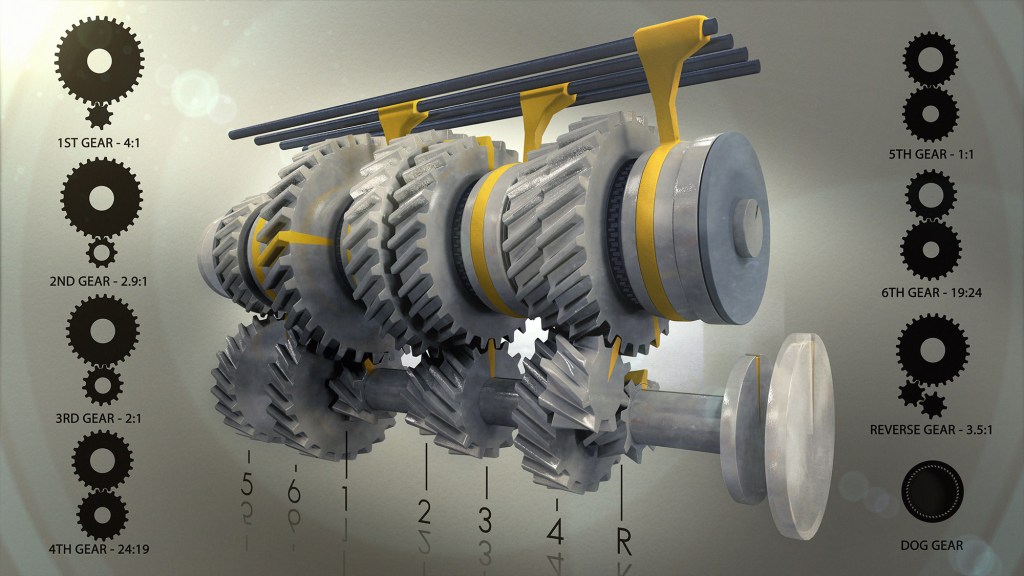
Gearset
Gear is a circular rotating part with several teeth in it. This is used to transmit the motion, i,e to increase or decrease the speed of the system according to the requirements. There are are many such gear (i,e 4 or 5).
Clutch
The job of a clutch is to engage and disengage power from the engine crankshaft to the transmission. Without this, the only way to engagement and disengagement of the gears is to by stopping the system.
Transmission Drive
There are three basic ways to transmit engine power to the rear wheel of a motorcycle: chain, belt or shaft. where the chain transmission is on the most commonly used form of transmission. The power developed in the engine is transmitted with the help of gear and shafts to the rear part of the motorcycle, and this power is also to be transmitted to the front wheel as well, this is where the drive transmission comes into picture and transmits the power.
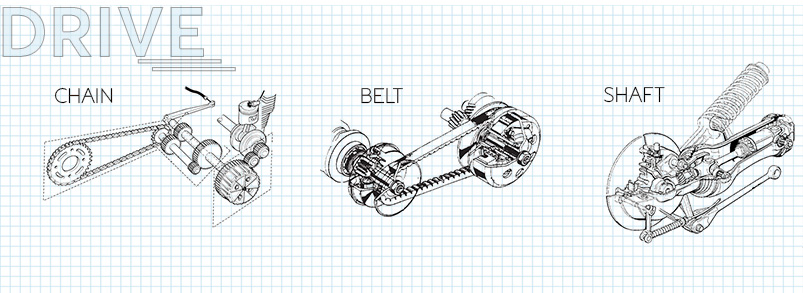
5. Electronic system
To power the electronic system two types of sources are used i,e BATTERY and ALTERNATOR
Battery: everyone knows battery very well. Here the battery is used to deliver Direct Current (DC) to the motorcycle’s electronics when the engine is turned off. Battery also provides the current to crank up the engine when you push that electric start button on the switchgear.
Alternator: The Alternator generates electricity once the engine is started. It utilizes the power of the engine’s crankshaft, to turn the magnets and produce electricity as an electromagnet flux is induced in it, the electricity is from it is also used to charge the battery. It is also used to convert the DC to AC.
The parts under working electronic systems are
- Lights/lamps: head lamp, tail lamp, indicators, Fog lamps etc,
- Digital meters: Speedometer, fuel indicators, Odometer etc,
- Horns
- Charging ports etc,
6. Suspension
suspension is provided to give smooth movement of the motorcycle and the driver, but cancelling the vibrations, caused by the humps and bumps on the roads. This system is provided on both the ends of the bike i,e on rear and front end of the bike.
Different types of suspension are as follows
- Telescopic suspension
- Spring loaded hydraulic suspension
Telescopic suspension: Telescopic suspension is used for the front suspension in almost every motorcycle today. A primary barrel and a slider bar are placed inside this suspension for giving non-vibrational movement. It is loaded with a spring and fork oil inside to give the shock absorbing facility.
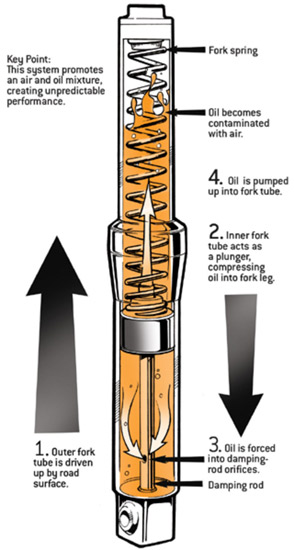
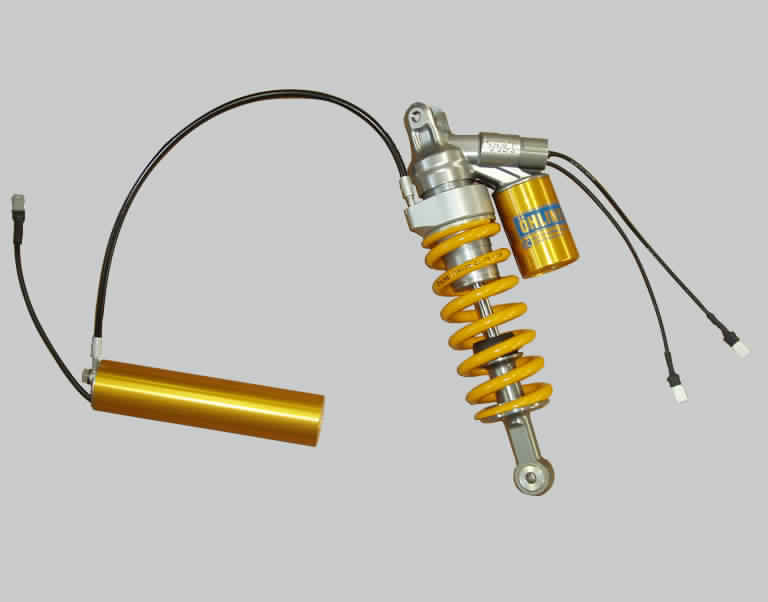
Spring loaded hydraulic suspension: This type of suspension is used for the rear suspension of the motorcycle. A liquid named damping oil is used as the suspension base for this suspension. This liquid is placed under a pressure of hydraulic piston and it is in air tied condition. Outside the suspension there is a spring and this spring ensures that after the spring piston gets downward because of the pressure it comes back again at is place.

7. Brakes
A device used for slowing or stopping a moving vehicle, to reduce the speed of the motorcycle or stop it, it is done by means of friction.
- Drum brake
- Disk brake
- Anti-lock braking system
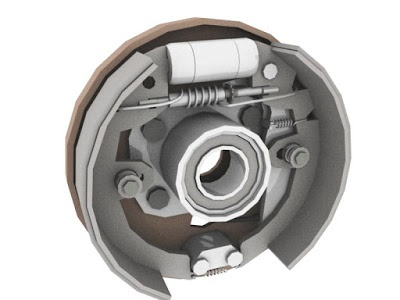
Drum brake: Earlier, this type of braking system was most common and are even used now, in some economical motorbikes. I consists of a circular hollow section, which protects the system from dust, moisture, and other stuff. it is made up of 2-curved plates, which acts as brake shoe for the system, that expands and contracts accordingly with the help of springs. due to the friction between the wheels and the brake shoe, the speed of the bike is slowed or can be stopped.
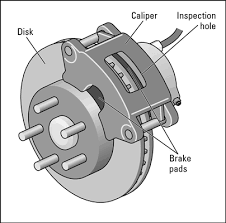
Disk brake: Disk brake consists of a cast iron disc bolted to the wheel hub and a stationary housing called caliper. The caliper is connected to a stationary part of the vehicle and it divided into two parts, each part containing a piston arrangement with a friction pads on both the ends. When the brakes are applied, hydraulically actuated piston move the friction pads into contact with the disc, causing the braking action. this action also liberates a large amount of heat,due to friction, therefore the disk is also provided with some vent holes at equal intervals across the circumference, to cool the disk by letting air to pass through it.
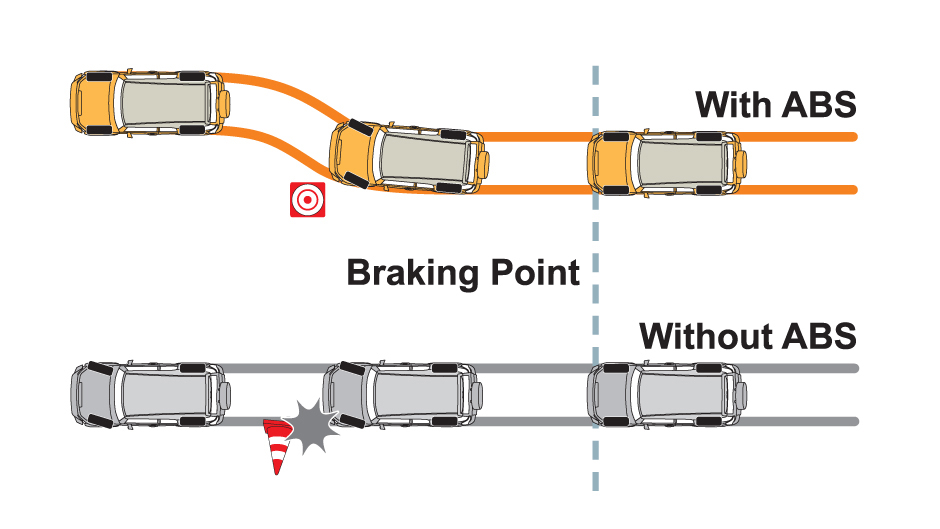
Anti-lock braking system (ABS): This is one of the modern, braking system. This type of system is used in high performance and sporty motorcycles, it expensive and very complex in functioning than others in this list. This system prevents the wheels from locking up and helps them maintain grip with the road below, unlike other two mentioned above.
ABS has a electronic system known as electronic stability control, which monitors wheels’ under braking. Each wheel has a sensor attached to it. If the sensors detect that a wheel is about to lock up and stop moving, the system will release the brake quickly, for a moment and holding it again. ABS then continuously and repeatedly applies optimum braking pressure to each wheel, so that it does not lock the wheels. This way the wheel will not lock and the driver will have control over the bike even when braking.
8. Wheels
wheels are circular blocks, that when rotating about the axis to provides motion/movement to the system. Earlier, this was made up of wood, as the time passed we used metallic materials, like iron, steel, etc. In this modern world use of alloy wheel, chrome wheels, etc are used ,were alloy wheels are most commonly used, but it is costlier relative to others. Motorcycle commonly are referred to as two-wheelers, I,e it contains 2-wheel.
it is basically made up of two component, i,e
Rim: It is a solid structure made up of steel, alloy, chrome etc, to provide support to the tire. It comes with different wheel disk structures and designs.
Tire: It a made up of natural rubber with many steel wire reinforcement. There are two types of of tires i,e tubeless tire and tubed tire
