Life is too Short to Drive Boring Cars.
Benz
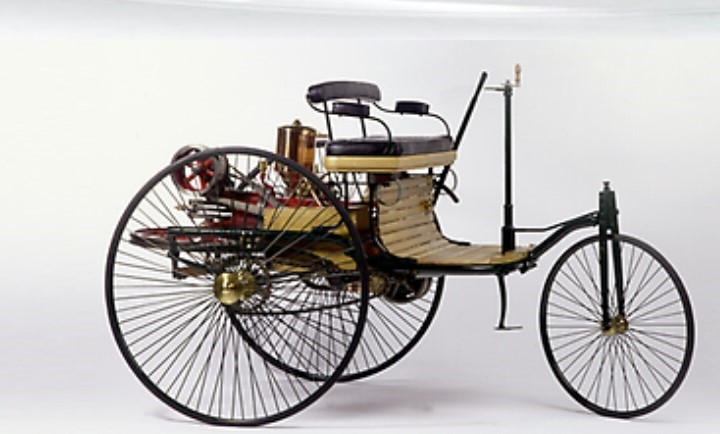

Benz motorwagen
Year-1886
Engine-1cyl, 954cc, 2 stroke
Fuel type-petrol (gasoline)
Ignition- trembler coil ignition
Power-500watts
Weight 100kg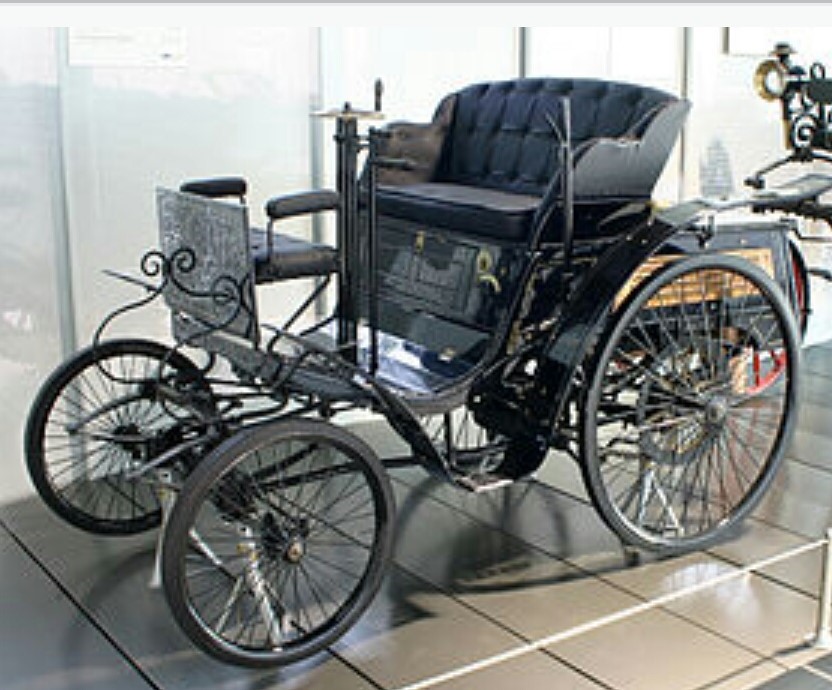
Benz velocipede
Year -1894
Fuel-petrol
Engine- 1lt, 1.5hp, 63.8cc,
Transmission-3 speed auto
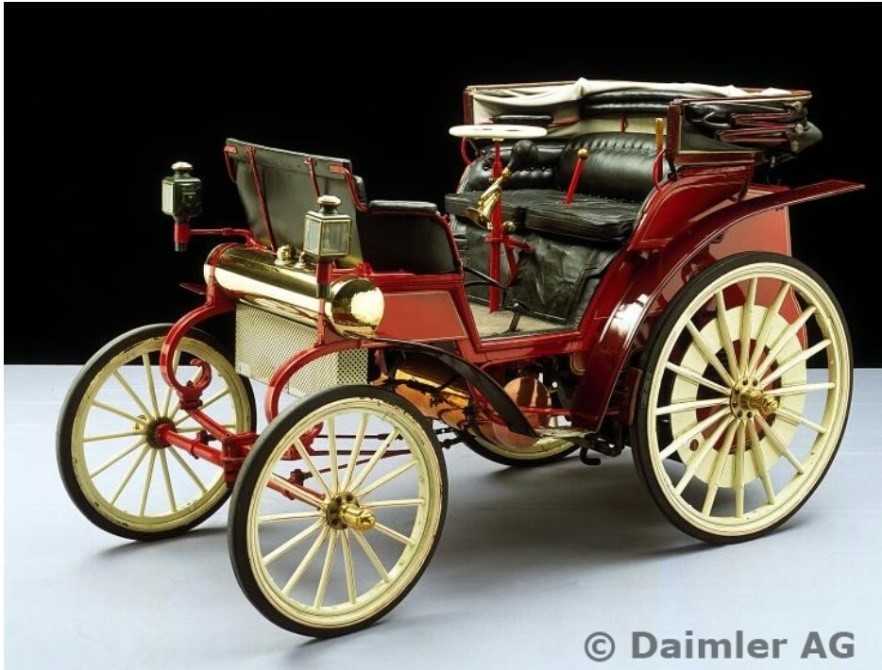

Daimler motor kutche AG
Year- oct 1892
Engine- 4hp, belt driven
Fuel- petrol
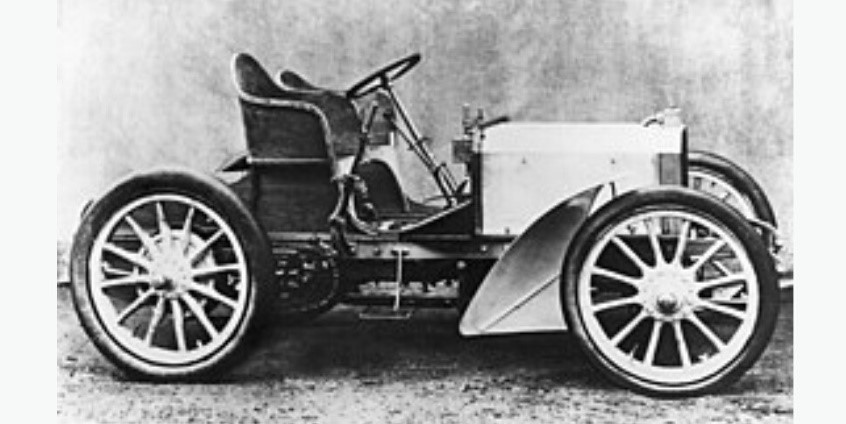
Mercedes 35ps
year-1901
Engine -5.916lt,35hp
Transmission- manual, 4 forward, 1reverse
Weight-1200kg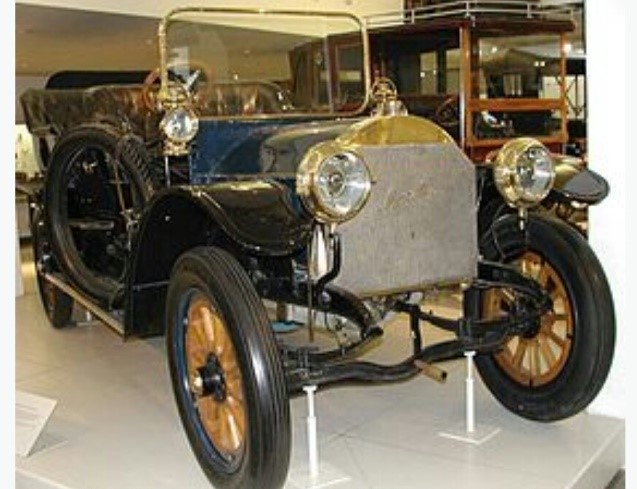
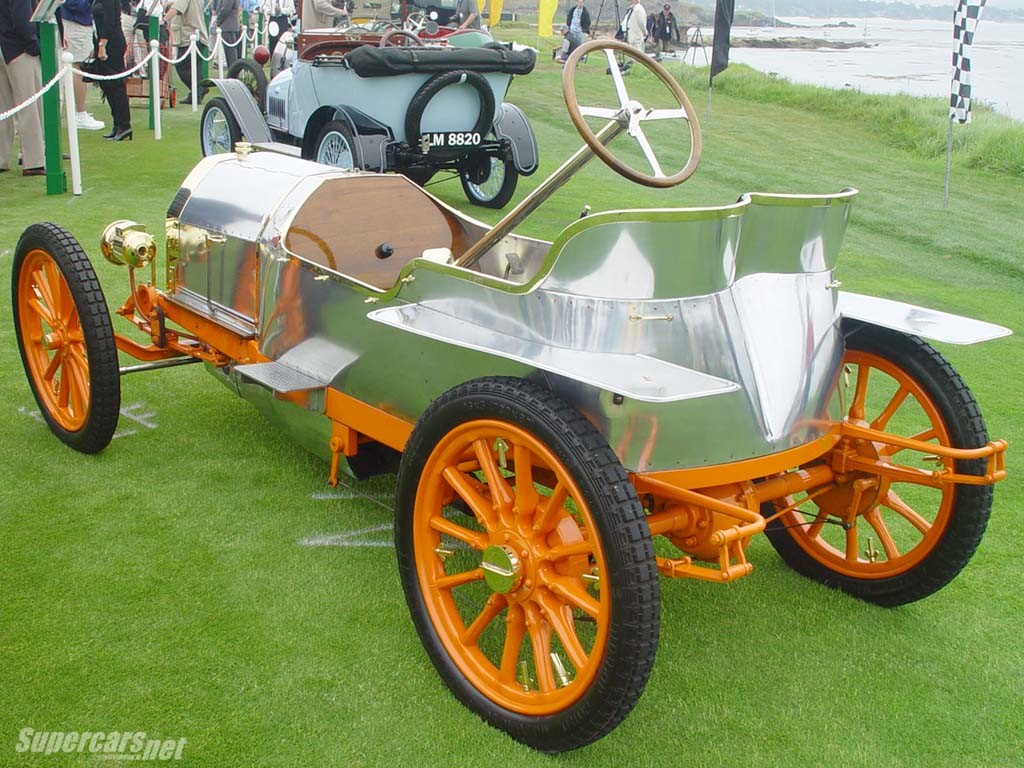
Mercedes simplex
Year-1902-1909
Engine-5315cc/9236cc, inline4, 41hp at 1050rpm
The engine produced 44 hp at 1300 rpm.
Its four cylinders featured:
water cooling
lubrication by driver-controlled pressure
120 mm bore and 150 mm stroke
valves mechanically timed by enclosed camshaft mechanically
engine displacement of 6786 cc
Trans,ission- manual, forward, 1reverse
Weight- 1200/1400kg
Mercedez benz ssk
Year-1928-1932
Engine- supercharged 7,069 cc (7.1 L) SOHC I6
Transmission-4-speed non-synchro-manual
Wight-3700kg
Class- sports
Type- coupe

Mercedez benz 770
Engine- 7,655 cc M07 I8 (1930–1938)
7,655 cc M150 I8 (1938–1943
Class-Full-size luxury car
Body style-4-door, 6-seat Pullman (limousine)
Touring car (6 seats) Cabriolet
Layout-FR layout
Mercedes benz W22
Engine-3,820cc Inline-eight engine
without or with “Kompressor” (Supercharger)
90 PS (66 kW; 89 hp), 120 PS (88 kW; 118 hp) or 140 PS (103 kW; 138 hp)
Also called Mercedes-Benz Typ 380
Mercedes-Benz 15/90 PS
Mercedes-Benz 15/120 PS
Mercedes-Benz 15/140 PS
Production 1933–1934
154 units
Assembly Stuttgart, Germany
Body and chassis
Class Large luxury car
Body style Torpedo bodied 2 door “Tourenwagen”
4 door “Limousine” (sedan/saloon)
Roadster
2 door Cabriolets (various)
Also listed in bare chassis form
Layout FR layout
Powertrain
Mercedes benz 500k
Engine 5,018 cc (5.018 L) I8
Transmission 4-speed manual
optional 5-speed manual
Body style- 2-door convertible
Layout FR layout
Powertrain
Weight -2700kg

Mercedes benz 540K
Powertrain
Engine 5,401 cc straight-8
Transmission 4-speed or optional 5-speed manual
Production 1936–1940 (chassis — last bodies completed in 1944)
Assembly Untertürkheim factory, Sindelfingen, Germany
Designer Friedrich Geiger
Body and chassis
Body style two seater cabriolet
four seater coupé
seven seater limousine
Layout FR layout
Mercedez benz 260-d
Powertrain
Engine 2545 cc OM138 I4 diesel
Transmission – three-speed gearbox with overdrive (Nullserie), four-speed with synchromesh on all ratios from 1937.
Production 1936–1940
Body and chassis
Class Full-size sedan
Body style 4-door sedan
landaulette
cabriolet
Layout FR layout
Mercedes benz w15
Also called Mercedes-Benz
Mercedes-Benz W15
Production 1931–1936
13,775 units
Assembly Germany: Stuttgart
Body and chassis
Class Mid-size car (D)
Layout FR layout
Powertrain
Engine 1,692cc

Mercedes benz 170k
Powertrain
Engine
1,697cc M136 I4 (1935-1950)
1,767cc M136 I4 (1950-1953)
Production 1935–1942
75,006 units
1947–1955
83,190 units
Assembly
Germany: Stuttgart
Argentina: Buenos Aires
Body and chassis
Class Mid-size car (D)
Body style 4-door sedan
4-door Cabrio-Limousine
2-door 2 & 4 seater cabriolets
2-door roadster
2-door pickup,4-door van
Layout FR layout
Mercedes benz w-125 rekredwagon
Grand Prix race car- 750 kg (1,653 lb)
GP car- 8-cylinder inline M125 V12 engine
Concept car s
Mercedes benz 320-A
Powertrain
Engine M142II, 85mm, 3405cm³
Production 1938–1942, Assembly Germany,Designer Max Sailer
Body and chassis
Class Sports car
Body style 2-door cabriolet
Layout FMR layout

Mercedes benz 300
Related Mercedes-Benz 300 S, Mercedes-Benz 300SL
Powertrain
Engine 2996 cc M186 SOHC I6
Transmission 4-speed manual
3-speed automatic
Production W186: 1951-1957
12,190 built[1]
W186 Saloon: 7,646 , W186 Cabriolet D: 642
Body and chassis
Class Full-size luxury car
Body style 4-door saloon
4-door phaeton
4-door cabriolet
4-door limousine
Layout FR layout
Platform Mercedes-Benz W186
Doors 4
Mercedes benz ponton
Engine
2,195 cc (2.2 L) M127 I6
2,195 cc (2.2 L) M180 I6
1,897 cc (1.9 L) M121 I4
1,767 cc (1.8 L) M136 I4
1,697 cc (1.7 L) OM636 I4
1,897 cc (1.9 L) OM621 I
Production 1953–1963
Assembly
West Germany: Stuttgart
Australia: Port Melbourne
South Africa: East London
Designer Fritz Nallinger
Body and chassis
Class
Mid-size executive / luxury car
Mid-size coupe / cabriolet
Body style
4-Door Sedan,4-Door Limousine,2-Door Coupe, 2-Door Convertible
Layout FR layout
Mercedez benz w189
Also called Mercedes-Benz 300d
Production W189 Saloon: 3,077
W189 Cabriolet D: 65
[1]
Body and chassis
Class Full-size luxury car
Body style 4-door saloon
4-door phaeton
4-door cabriolet
4-door limousine
Layout FR layout
Platform Mercedes-Benz W189
Related Mercedes-Benz 300 Sc, Mercedes-Benz 300SL
Powertrain
Engine 2996 cc M189 I6
Transmission 4-speed manual
3-speed automatic >

Mercedes benz w194
3.0 litre SOHC straight-6,
Category- endurance racing
Mercedes benz 300sl
Powertrain
Engine 2,996 cc (182.8 cu in) M198 Straight six
Transmission 4-speed manual
Production 1954-1957 (Coupe)
1957–1963 (Roadster)
3,258 built[1]
Coupé: 1,400
Roadster: 1,858
Assembly West Germany: Stuttgart-Untertürkheim
Body and chassis
Class Sports car / Grand tourer
Body style 2 door coupe, roadster
Layout FR layout
Platform Mercedes-Benz W198
Doors Gull-wing doors
Related Mercedes-Benz W121 BII (190 SL)
Mercedes benz 190sl
Powertrain
Engine 1,897 cc M121 SOHC I4
Transmission 4-speed manual, fully synchronized
Production 1955–1963
25,881 built[1]
Assembly West Germany: Stuttgart Untertürkheim
Body and chassis
Class Sports car / Grand tourer
Body style roadster
Layout FR layout
Platform Mercedes-Benz W121
Related Mercedes-Benz W198 (300 SL)
Mercedes-Benz W120/121 rm

Mercedez benz w111
Manufacturer Mercedes-Benz
Production Sedan: 1959–1968
Coupe: 1961–1971
370,807 built
Assembly
West Germany: Stuttgart
Australia: Port Melbourne[1]
Designer Friedrich Geiger
Body and chassis
Class Full-size luxury car (F)
Body style 4-door sedan
2-door coupé
2-door convertible
Layout FR layout
Related Mercedes-Benz W110
Mercedes-Benz W112
Mercedes-Benz W113
Powertrain
Engine 2,195 cc (2.2 L) M127 I6 2,306 cc (2.3 L) M180 I6 2,496 cc (2.5 L) M129 I6 2,778 cc (2.8 L) M130 I6 2,996 cc (3.0 L) M189 I6 3,499 cc (3.5 L) M116 V8
PREDESSOR- PONTON
Mercedes benz w100(600)
Powertrain
Engine 6.3 L M100 V8
6.8 L M100 V8
Is also called Grand Mercedes Der Große Mercedes
Production
1963–1981 2,677 built[1] SWB: 2,190 LWB: 428
Landaulet: 59
Designer- Bruno Sacco Friedrich Geiger Paul Bracq
Body and chassis
Class Ultra-luxury car (F)
Body style
4-door sedan (SWB)
4-door limousine
6-door limousine
Landaulet limousine
Layout FR layout
Mercedes-Benz W112
Powertrain
Engine 2,308 cc (2.3 L) M127.II SOHC I6
2,496 cc (2.5 L) M129.II SOHC I6
2,778 cc (2.8 L) M130 SOHC I6
Transmission 4-speed automatic
4-speed manual, 5-speed ZF S5-20 manual
Production 1963–1971
48,912 built[1]
Assembly West Germany: Stuttgart Untertürkheim
Designer Paul Bracq
Béla Barényi
Friedrich Geiger
Body and chassis
Class Sports car / Grand tourer
Body style 2 door coupé
2-door roadster
Layout FR layout
Platform Mercedes-Benz W111
Related Mercedes-Benz W108
Mercedes-Benz W109

Mercedes benz s-class
Production Predecessors date to 1954
S-Class nomenclature adopted in 1972
Assembly Sindelfingen, Germany
Pune, India[1]
Samut Prakan, Thailand[2]
Pekan, Malaysia[3]
Bogor, Indonesia[4]
Body and chassis
Class Full-size luxury car (F)
Body style 4-door sedan
2-door coupé
Related Mercedes-Benz CL-Class
Mercedes-Benz CLS-Class serify
MB 300sel 6.3
Production 1968–1972
Body and chassis
Class Full-size luxury car (F)
Layout FR layout
Platform Mercedes-Benz W109
Powertrain
Engine 6,332 cc (386.4 cu in) M100 V8
Transmission 4-speed automatic
MB 450 sel 6.9
Production 1975–1981
Body and chassis
Class Full-size luxury car (F)
Platform Mercedes-Benz W116
Powertrain
Engine 6.834 L M100 V8 Transmission 3-speed automatic

Mb W114/115 (new generation concepts)
Powertrain
Engine
2.0 L M115 I4 (petrol) 2.2 L M115 I4 (petrol) 2.3 L M115 I4 (petrol) 2.3 L M180 I6 (petrol) 2.5 L M114 I6 (petrol) 2,746 cc M110 I6 (petrol) 2,778 cc M130 I6 (petrol) 2.0 L OM615 I4 (diesel) 2.2 L OM615 I4 (diesel) 2.4 L OM616 I4 (diesel) 3.0 L OM617 I5 (diesel)
Transmission
4-speed 722.1 automatic
4-speed 722.2 automatic
Also called Mini / Mercedes Mini (Indonesia)
Production 1968–1976
1,919,056 built
Saloon: 1,852,008
Coupé: 67,048
Assembly
West Germany: Stuttgart West Germany: Bremen West Germany: Sindelfingen South Africa: East London, South Africa Portugal: Setúbal (Movauto) Venezuela: Barcelona (CKD) Argentina: González Catán
Designer Paul Bracq
Body and chassis
Class Executive car (E)
Body style 4-door sedan
2-door coupé 4-door limousine Layout FR layout
Mb C11
Powertrain
Engine 2.4 L Four-rotor Wankel engine
Transmission 5-speed manual
Production 1970 (16 cars produced)
Assembly Untertürkheim
Designer Bruno Sacco
Body and chassis
Class Sports car
Body style 2-door berlinetta
Layout Transverse, Rear mid-engine, rear-wheel drive
Doors Gullwing doors
Mb SL(R107) SLC(C107)
Powertrain
Engine I6 2.8L (SL, SLC) 3.0L (SL)V8 3.5L (SL, SLC) 3.8L (SL, SLC) 4.2L (SL) 4.5L (SL, SLC) 5.0L (SL, SLC) 5.6L (SL)
Transmission Automatic
3-speed 722.0 350SL/SLC 450SL/SLC 4-speed 722.1 280SL/SLC 4-speed 722.2 350SL/SLC 450SLC 4 speed 4G-TRONICManual 4 speed (280/350 SL/SLC) 5 speed (280/300 SL/SLC)
Production SL: 1971–1989
SLC: 1971–1981
300,175 built[1]
SL: 237,287
SLC: 62,888
Model years SL: 1971–1989
SLC: 1972–1981
Assembly
West Germany: Sindelfingen
South Africa: East London (CKD)
Designer Joseph Gallitzendörfer; Friedrich Geiger (1968)
Body and chassis
Class Sports car/Grand tourer
Body style two-door roadster
two-door coupe
Layout FR layout

MB w123
Powertrain
Engine 2.0 L M115 V20 I4 2.0 L M102 V20 I4 2.3 L M115 V23 I4 2.3 L M102 E23 I4 2.5 L M123 I6 2.8 L M110 I6 2.0 L OM615 D20 diesel I4 2.2 L OM615 D22 diesel I4 2.4 L OM616 diesel I4 3.0 L OM617 diesel I5 3.0 L OM617 A td I5
China: 2.4 L BJ492 I4 (petrol)
Transmission 4-speed 722.1 automatic 4-speed 4G-TRONIC automatic 4-speed manual 5-speed manual
Also called Kaensaeng 88 (North Korea)
Production 1976–1986
2,696,915 built[1] 4-door: 2,375,410 Coupé: 99,884
Estate: 199,517 Limousine: 13,700 Chassies: 1,353 LWB chassies: 7,020
Assembly
West Germany: Sindelfingen
West Germany: Stuttgart
West Germany: Bremen
South Africa: East London (sedan only)
China: Changchun (FAW, 1987–1988)[2]
Designer Bruno Sacco, Friedrich Geiger (Saloon & coupe: 1973, T-Model: 1975)
Body and chassis
Class Executive car (E)
Body style 4-door saloon
2-door coupé (C123) 5-door estate (S123) 4-door limousine (V123)
Layout FR layout
MB w124
Powertrain
Engine Petrol I4[show] I6[show] V8[show] Diesel I4[show] I5[show] I6[show]
Transmission Automatic, 4-speed 4G-TRONIC ,5-speed 722.5Manual, 4-speed (floor or column), 5-speed (floor)
Production
November 1984–August 1995 (sedan) October 1985–June 1996 (estate) April 1987–late 1996 (coupé)
March 1992–July 1997 (convertible)
Model years
1985–1996
2,562,143 built
Assembly
Germany: Bremen, Germany: Rastatt , Germany: Sindelfingen Germany: Zuffenhausen, South Africa: East London, India: Pune (TELCO)[1], Mexico: Toluca[2], Poland: Karczew[3] , Indonesia: Bogor, Wanaherang Malaysia: Johor Bahru (OASB)[4]
Designer
Joseph Gallitzendörfer and Peter Pfeiffer (initial design)
Bruno Sacco (final design)[5][6]
Body and chassis
Class Executive car (E)
Body style
4-door saloon 5-door estate 2-door coupé 2-door convertible 6-door limousine
Layout Front engine, rear-wheel drive / four-wheel drive rial
MB w116
Powertrain
Engine 2.8L I6 3.5L V8 4.5L V8 6.9L V8 3.0L I5 turbodiesel
Transmission 3-speed 722.0 automatic 4-speed 722.1 automatic 4-speed manual 5-speed manual
Production 1972–1980
Assembly
West Germany: Sindelfingen
Venezuela: Barcelona (CKD)
Designer Friedrich Geiger (1969)[1]
Body and chassis
Class Full-size luxury car (F)
Body style 4-door sedan
Layout FR layout

MB w126
Powertrain
Engine Straight-5
3.0 L OM617 diesel,Straight-6 2.6 L M103 2.8 L M110 3.0 L M103 3.0 L OM603 diesel
3.5 L OM603 diesel V8 3.8 L M116 4.2 L M116 5.0 L M117 5.5 L M117
Transmission 4-speed 4G-TRONIC automatic
4-speed manual 5-speed manual
Production
December 1979 – April 1992 (sedan)
September 1981 – October 1991 (coupé)
?–1994 (sedan, South Africa)
Assembly Germany: Sindelfingen
Malaysia: Johor Bahru (OASB)[1]
South Africa: East London
Designer Bruno Sacco (sedan: 1975, 1976; coupe: 1977)
Body and chassis
Class Full-size luxury car (F)
Grand tourer (C126)
Body style 4-door sedan
2-door coupé (C126)
Layout FR layout
Related Monteverdi Tiara
MB w(201)
Engine Petrol:
1.8, 2.0, 2.3 L M102 8V I4 2.3, 2.5 L M102 16V I4 2.6 L M103 I6 3.2 L M103 AMG I6
Diesel: 2.0, 2.2 L OM601 I4 2.5 L OM602 I5 diesel 2.5 L OM602 Turbo-diesel I5
Transmission 4-speed manual 5-speed manual 4-speed 4G-Tronic automatic
Also called
Kaengsaeng 88 (North Korea, 1990–94, German CKDs)
Pyeonghwa 410 (North Korea, 1994–02, Indian CKDs)
Baby Benz
Production September 1982 – April 1993
1,874,668 produced[1][2]
Assembly
Germany: Bremen Germany: Sindelfingen Poland: Jelcz-Laskowice Thailand: Thonburi
Designer
Peter Pfeiffer Bruno Sacco (1979)
Body and chassis
Class Compact executive car (D)
Body style 4-door saloon
Layout Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive
MB w140
Powertrain
Engine Petrol: 2.8 – 3.2 L M104 I6 4.2 – 5.0 L M119 V8 6.0 L M120 V12 7.0 – 7.3 L M297 AMG V12
Diesel: 3.0 L OM606 td I6 3.5 L OM603 td I6
Transmission 4-speed 4G-Tronic automatic 5-speed 5G-Tronic automatic 5-speed manual
Production April 1991 – September 1998 (sedan)
October 1992 – September 1998 (coupe)
Assembly Germany: Stuttgart
Mexico: Toluca
Designer Olivier Boulay (Sedan exterior: 1986; Coupe exterior: 1987)
Bruno Sacco (design director 1982–1990)[1][2]
Body and chassis
Class Full-size luxury car (F)
Body style 4-door sedan (W140; short)
4-door sedan (V140; long)
4-door sedan (VV140; Pullman)
2-door coupé (C140)
Layout FR layout
Related Maybach 57 and 62
SsangYong Chairman H

Mb W220
Powertrain
Engine- 2.8 L 201 hp (150 kW) V6 3.2 L 221 hp (165 kW) V6 3.2 L 194 hp (145 kW) I6 Diesel 3.2 L 201 hp (150 kW) I6 Diesel 3.7 L 242 hp (180 kW) V6 4.0 L 247 hp (184 kW) V8 Diesel 4.0 L 256 hp (191 kW) V8 Diesel 4.3 L 275 hp (205 kW) V8 5.0 L 302 hp (225 kW) V8 5.4 L 355 hp (265 kW) V8 5.4 L 493 hp (368 kW) AMG V8 5.8 L 362 hp (270 kW) V12 6.3 L 438 hp (327 kW) V12 5.5 L 493 hp (368 kW) V12 twin-turbo 6.0 L 604 hp (450 kW) AMG V12
Transmission 5-speed automatic 7-speed automatic
Production August 13, 1998 – July 20, 2005
Model years
1999–2005
2000–2006 (North America)
Assembly
Germany: Sindelfingen
Mexico: Toluca
Indonesia: Bogor[1]
Designer Steve Mattin, Bruno Sacco [2] (1995)
Body and chassis
Class Full-size luxury car (F)
Body style 4-door sedan
Layout Front engine, rear-wheel drive / four-wheel drive
Related Mercedes-Benz C215
MB r-129 (fourth generation)
Engine 2.8 L 193 hp (144 kW) I6 2.8 L 204 hp (152 kW) V6 3.0 L 190 hp (142 kW) I6 3.0 L 231 hp (172 kW) I6 3.2 L 231 hp (172 kW) I6 3.2 L 224 hp (167 kW) V6 5.0 L 326 hp (243 kW) V8 5.0 L 306 hp (228 kW) V8 5.5 L 354 hp (264 kW) AMG V8 6.0 L 381 hp (284 kW) AMG V8 6.0 L 394 hp (294 kW) V12 7.0 L 496 hp (370 kW) AMG V12 7.3 L 518 hp (386 kW) AMG V12
Transmission 5-speed automatic 4-speed automatic 5-speed manual
MB sl320
1989 Mercedes SL
Engine- 228 hp (170 kW) 3.0-litre inline 6
300 SL version in the US. In Europe
Engine-190 hp (140 kW) 3.0-litre inline 6
Special edition
300 SL with 12 valves, and the 228 hp (170 kW)
3.0-litre inline 6 with 24 valves is known as the 300 SL 24 .
326 hp (240 kW) 500 SL (with a 5.0 L V8 engine)

MB g-class
also called
Mercedes-Benz G-Wagen (1979–present)
Puch G
Production
SUV: 1979–present
Pickup truck: 2013–2015 (69 made)
Assembly
Austria: Graz
Algeria: Tiaret (200 BA6 G Class)[1]
Greece: Thessaloniki[2]
Body and chassis
Class
Mid-size[3] luxury SUV
Heavy duty luxury pickup truck
MB r230 (fifth generation)
Powertrain
Engine 3.7 L 245 hp (183 kW) V6 5.0 L 302 hp (225 kW) V8 5.4 L 493 hp (368 kW) V8 6.0 L 604 hp (450 kW) V12
Transmission 5-speed automatic 7-speed automatic
Production 2001–2011
Body and chassis
Fifth generation facelift MB r230
Engine 5.0 L 308 hp (230 kW) V8 5.4 L 493 hp (368 kW) V8 5.5 L 382 hp (285 kW) V8 6.0 L 604 hp (450 kW) V12 6.2 L 518 hp (386 kW) V8
Transmission 5-speed automatic
7-speed automatic

6TH GENERATION( MB R231 PLATFORM)
Engine 3.0 L 333 PS (245 kW) – 362 PS (266 kW) V6 Biturbo
3.5 L 302 hp (225 kW) V6
4.7 L 430 hp (321 kW) V8 turbocharged
5.5 L 429 hp (320 kW) V8 turbocharged
6.0 L 621 hp (463 kW) V12 turbocharged
Transmission 7-speed automatic (9-speed from MY2017)
YEAR- 2012 and present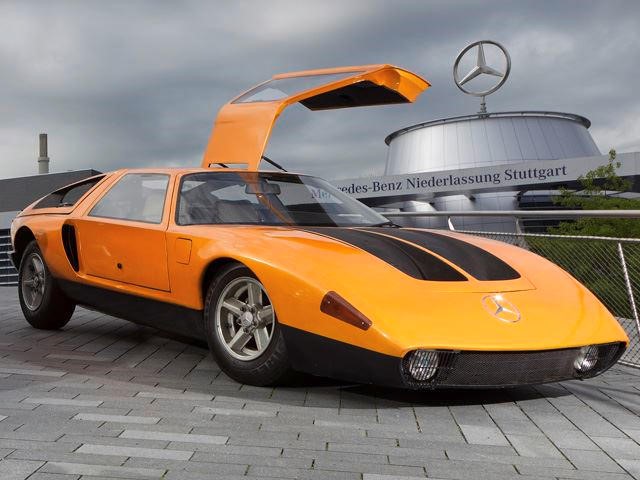
C111
1960s and 70s when Mercedes experimented with a prototype called the C111. A rolling test-bed, the C111 used a variety of engines over the course of its lifetime, including a Wankel rotary, a diesel and a twin-turbo V8. By the time the program was done, the C111 research vehicle claimed a number of speed records, reaching a massive 251 mph in 1979. It would take decades until the Bugatti Veyron would beat that speed at nearly 254 mph, but while Mercedes toyed with the idea of a production version, it ultimately never made any for public consumption.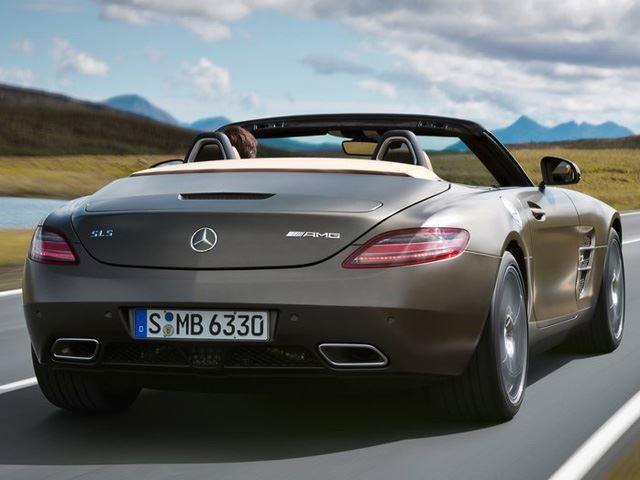
SLS
SLS is a modern tribute to the original 300 SL, but while the SLS carries the classic’s gull-wing doors and some retro styling, there’s nothing outmoded about the SLS. The SLS AMG launched over three years ago with a 6.2-liter V8 packing 563 horsepower, and has since bred numerous derivatives: the Roadster, the upgraded GT, the Black Series and the Electric Drive. But even in its most “basic” form, the SLS can run to 60 in under four seconds and top out at over 200 mph.
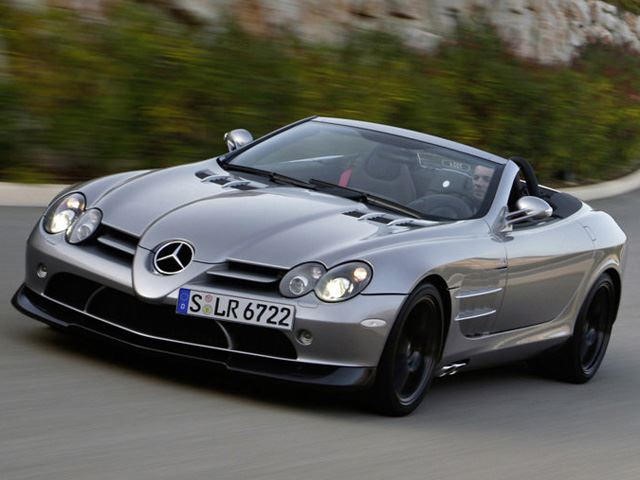

The SLR
a racing-inspired supercar with Mercedes levels of luxury and refinement. Its 5.4-liter supercharged V8 churned out 617 horsepower to send the carbon-fiber super-GT to 60 in 3.4 seconds. Like the SLS, the SLR family expanded to include a Roadster, the 722 edition, the Stirling Moss speedster and numerous combinations thereof. Ultimately it proved the
last time Mercedes and McLaren would collaborate, as the former sold its stake in the latter, which in turn went its own way with the MP4-12C and the new P1.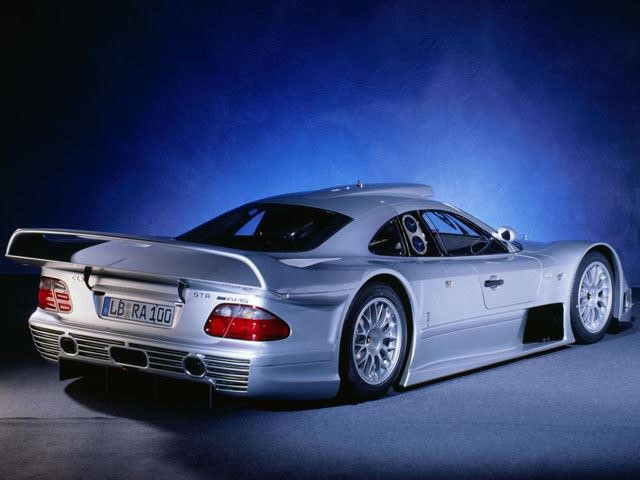
Mercedes-Benz CLK GTR.
While it may have looked like the coupe with which it shared its name, the similarities were only skin-deep, retaining only the instruments and headlamps from the luxury coupe. It packed a 6.9-liter V12 smack in the middle, sending over 600 horsepower to the rear wheels for a 3.8-second 0-60 time and a 200 mph top speed. Only 25 were made, including 5 roadster versions, each selling for over $1.5 million. The Sultan of Brunei bought the only two in right-hand drive.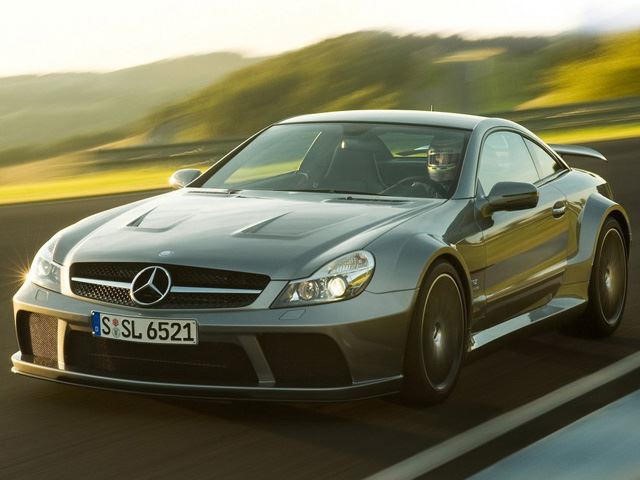
The SL65 AMG black
Black Series served as Mercedes’ flagship performance model. Based on the fifth-generation SL, the Black Series ditched the heavy folding hard-top in favor of a fixed roof and upgraded with such enhancements as bigger spools for the 6.0-liter twin-turbo V12, improved breathing, lighter body panels, a beefed-up suspension, bigger wheels and tires and upgraded brakes. With 661 horsepower, the SL65 Black was more potent than the SLS or the SLR, standing as the most powerful production Mercedes sportscar to date.
BUGGATTI

Bugatti Type 1
The Type 1 was an automobile designed by Ettore Bugatti and produced by Prinetti & Stucchi in 1899. It had four engines, two on each side of the rear axle.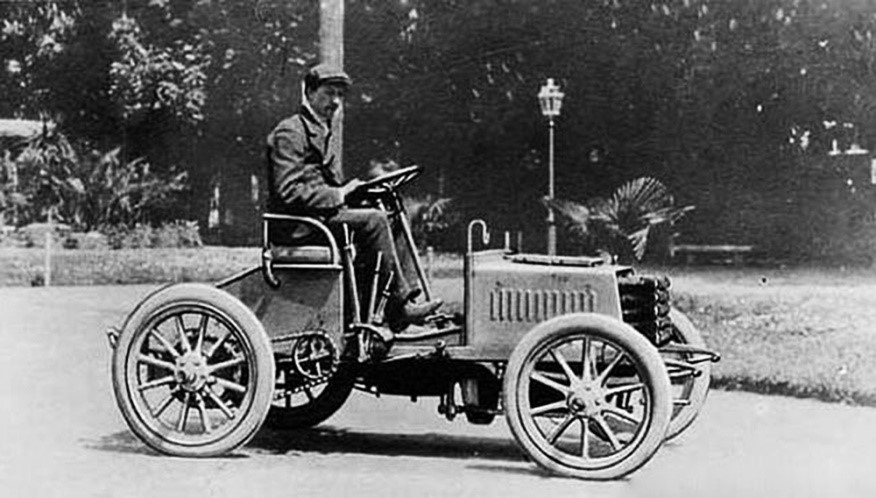
Type 2
Engine-3.1-liter inline-4 engine,
Wight-1,433-pound
Top speed- 37 mph.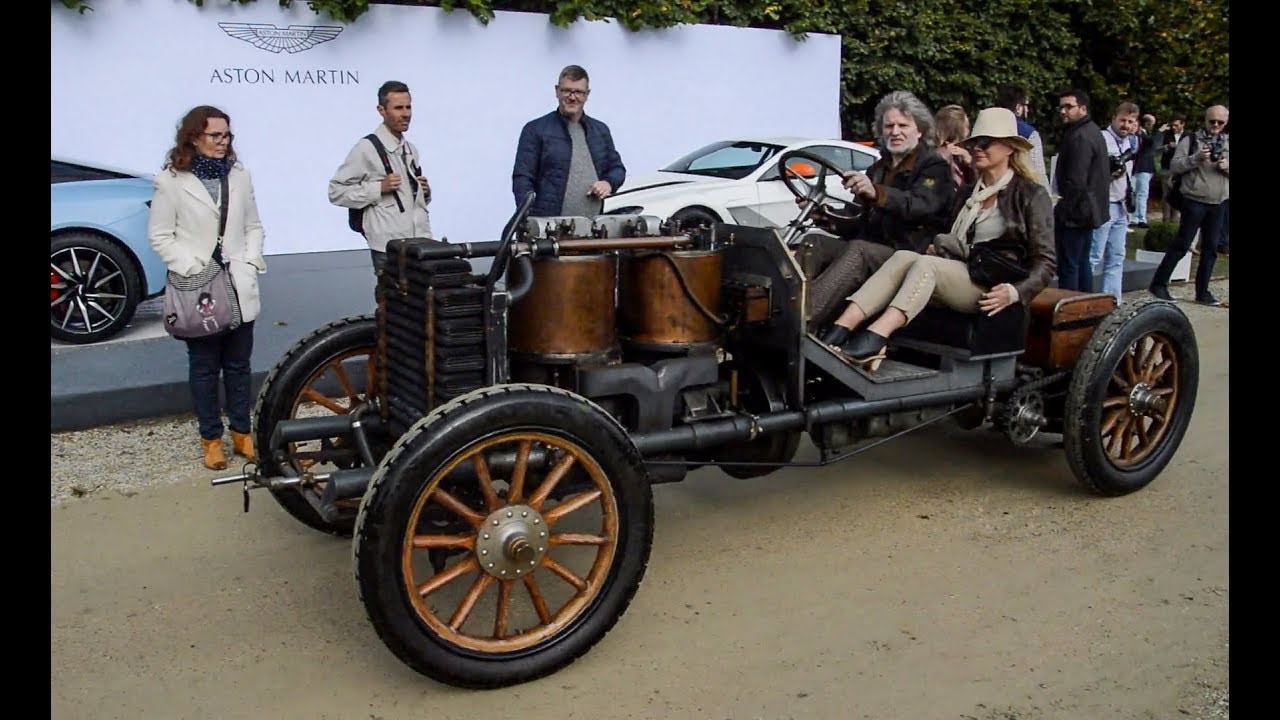
Type 5
Engine-12.9L 4-cylinder inline engine, 45 hp
Transmission- 4-speed manual transmission.
Engine- 1.1 L (1131 cc/69 in3) monobloc straight-four cylinder ,
overhead cam unit with two valves per cylinder,
60 mm bore and 100 mm stroke
open body with solid axles front and rear.
Leaf springs suspended the front with no suspension at all in the rear.
Cables operated rear drum brakes. ,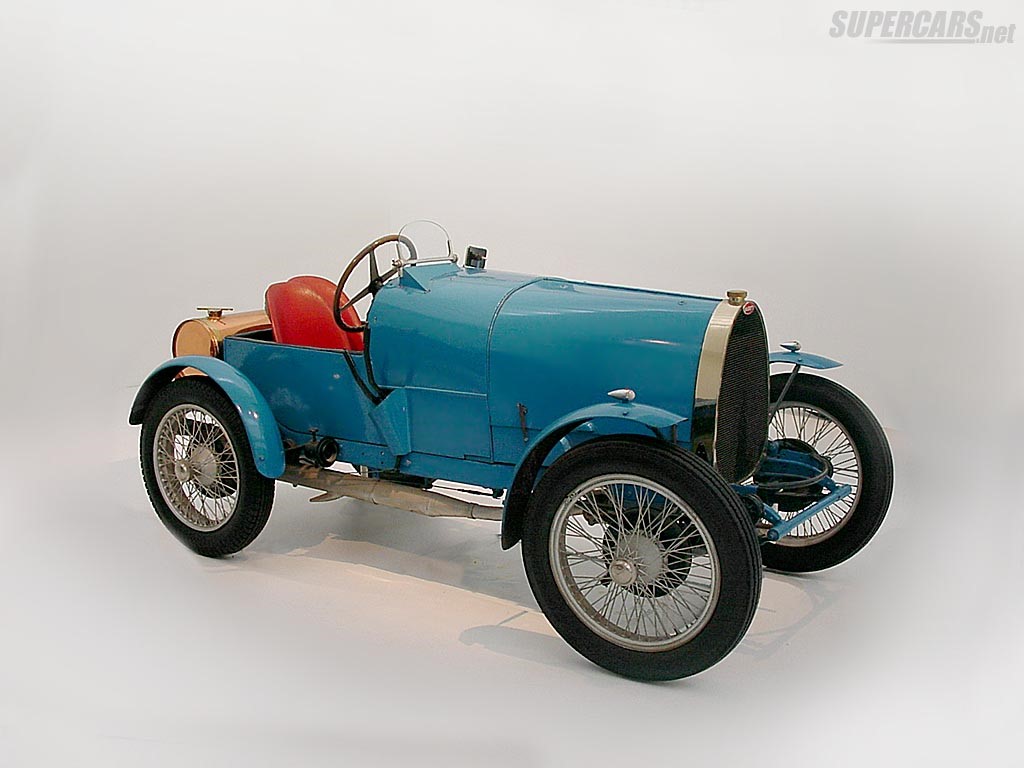
Chassis-Refined light shaft-driven, Leaf springs, 2 m (79 in) wheelbase
Engine- boring the engine out to 65 mm for a total of 1.4 L (1368 cc/83 in3), 4-valve head
Power – dual Zenith Carburetters with 30 hp (22 kW) at 4500 rpm.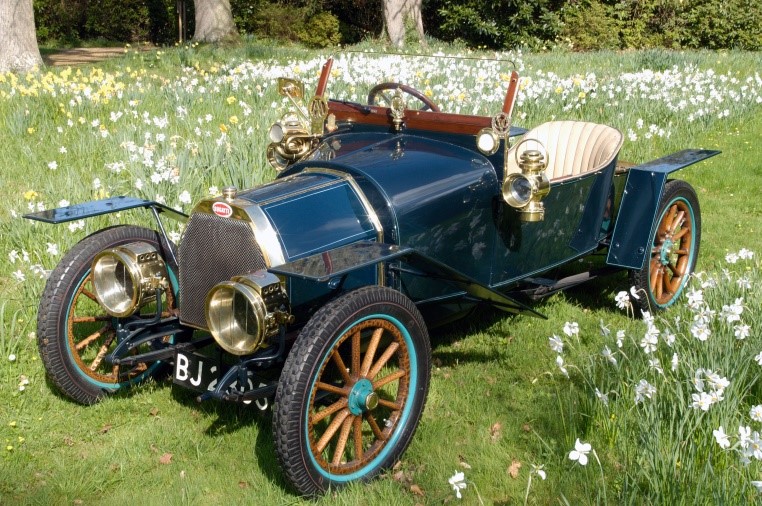
Engine-1.4 L (1368 cc/83 in3), 4-valve head
Chassis- 2400 mm (94.5 in), wheelbase, six-sided radiator in front and semi-elliptic rear leaf springs.

Engine- 5,027 cc with a bore and stroke of 100 by 160 mm.
Year-1912
Chassis and configuration- rear wheels drive
Bugatti twin chain transmission
reversed quarter-elliptic rear suspension springs
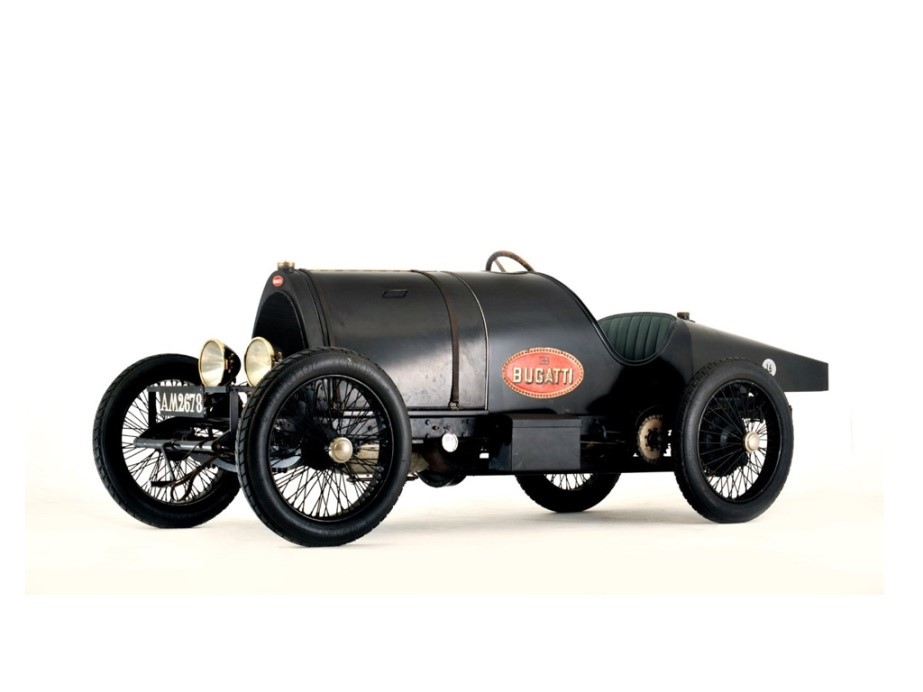
Engine-1.4 L (1368 cc/83 in3), 4-valve head
Chassis- 2550 mm (100.4 in) wheelbase, hexagonal radiator and rear springs of type 15
production 1912-1914
Powertrain
Engine 5,027 cc (307 cu in) Straight-4
Transmission four-speed sliding-pinion gearbox
final drive by side chains
Dimensions
Wheelbase 100.4 in (2,550.2 mm)
Track 49.2 in (1,249.7 mm)
Kerb weight 2,750 lb (1,247 kg)

Engine 900cc 4cyl
Wheelbase 2570 mm Width 1230 mm
Height 1560 mm
Engine-1.4 L (1368 cc/83 in3), 4-valve head
Year-1925
Updated version of type15
Chassis- road going body, an oval radiator, and quarter-circle springs.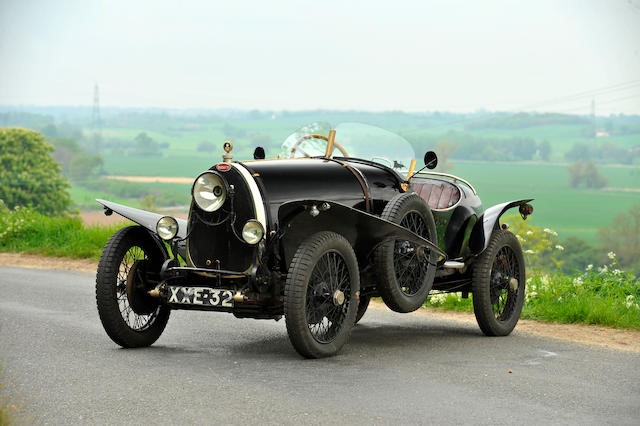
bresica tourer
Engine- single-overhead-camshaft,16-valve Brescia engine alongside 8-valve.
Year-1925
Updated version of type15
Chassis- road going body, an oval radiator, and quarter-circle springs
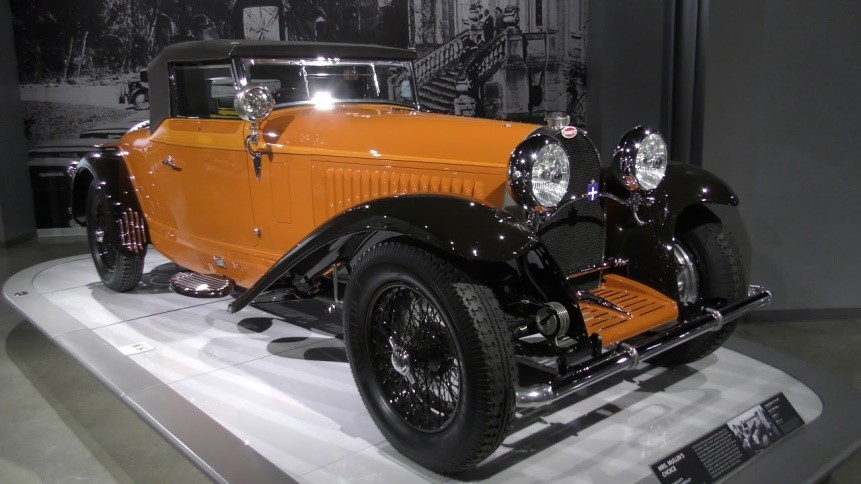

Year 1930
Category- luxury sports
Engine- unknown
Year 1930
Engine- 16 valve,1500cc engine
Top speed- 110kmph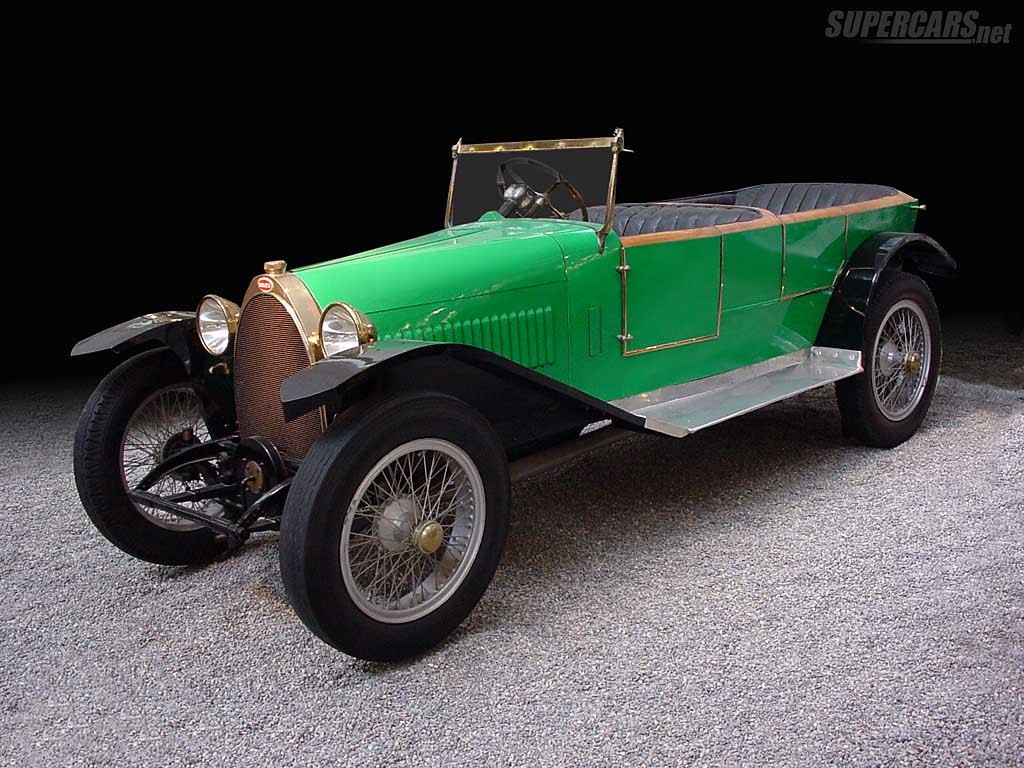
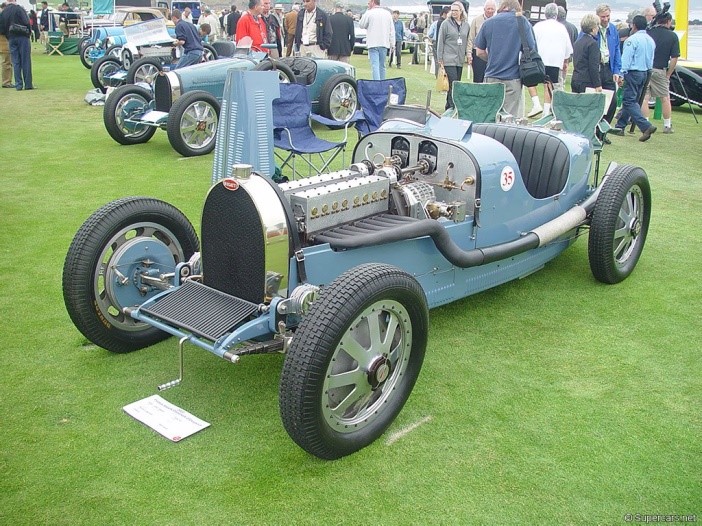
engine Inline-8
position Front Longitudinal
aspiration Natural
valvetrain 3 Valves per Cyl
displacement 2995 cc / 182.8 in³
bore 69 mm / 2.72 in
stroke 100 mm / 3.94 in
power 67.1 kw / 90 bhp @ 3400 rpm
specific output 30.05 bhp per litre
body / frame Light Pressed Steel w/Hardwood Filling
driven wheels RWD
front brakes Drums
f brake size mm / in
rear brakes Drums
r brake size mm / in
f suspension Solid Axle w/Half-Elliptic Leaf Springs
r suspension Rigid Axle w/Reversed Quarter-Elliptic Leaf Springs
wheelbase 2600 mm / 102.4 in
transmission Rear Mounted 2-Speed Manual
gear ratios :1
top speed ~130.4 kph / 81.0 mph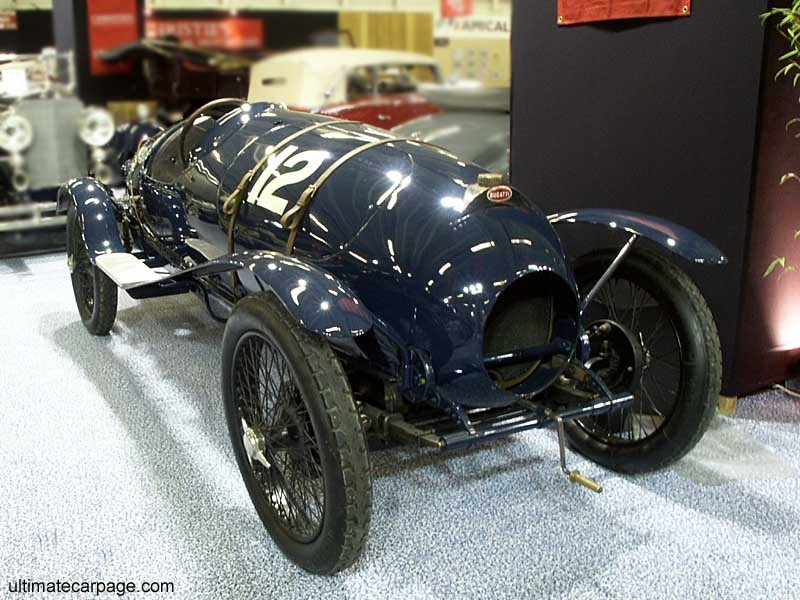
engine Inline-8
position Front Longitudinal
aspiration Natural
valvetrain OHV 3 Valves per Cyl
displacement 1991 cc / 121.5 in³
bore 60 mm / 2.36 in
stroke 88 mm / 3.46 in
power 44.7 kw / 60 bhp
specific output 30.14 bhp per litre
body / frame Steel over Steel Chassis
driven wheels RWD
front brakes Hydraulic Drums
f brake size mm / in
rear brakes Drums
r brake size mm / in
f suspension Solid Axle w/Half-Elliptic Springs
r suspension Live Axle w/Reversed Quarter Elliptic Springs
wheelbase 2550 mm / 100.4 in
gear ratios :1 ports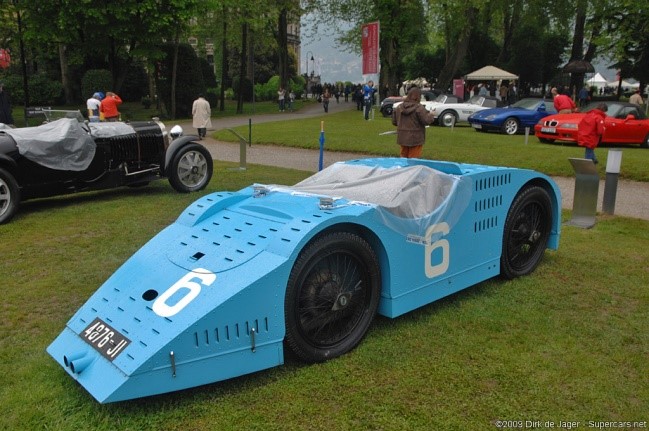
Engine- 2.0 L (1991 cc/121 in³) straight-8
Wheelbase: 78.5 in (1994 mm)
Track: 41.4 in (1052 mm)
Power: 90 hp (67 kW)
Engine- De-bored(to 52 mm) for a total displacement of 1.5 L (1494 cc/91 in³).
Length: 3680 mm (144.9 in)
Width: 1320 mm (52 in)
Wheelbase: 2400 mm (94.5 in)
Track: 1200 mm (47.2 in)
Weight: 750 kg (1650 lb)

Year 1925
Also called telca was just updated version of 35
While 35c was a supercharged version
Year 1927
Engine- 2.3 L of the Type 35T, supercharged.
Power-138 hp (102 kW), body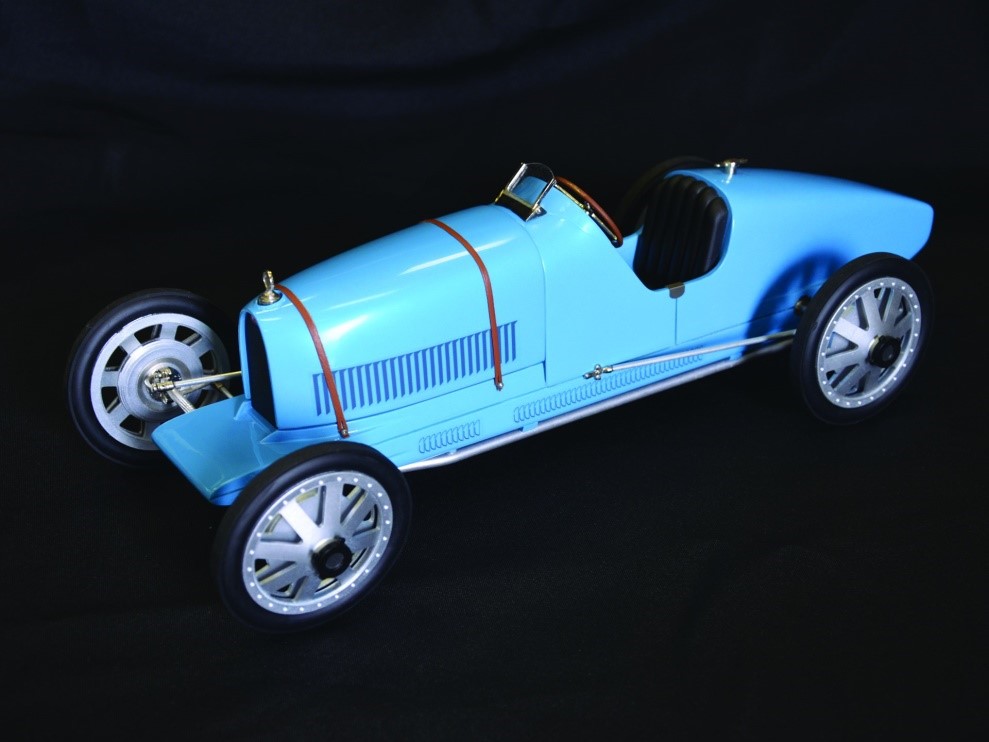
Year 1925
Engine- 1.5 L (1493 cc/91 in³) straight-8, 60 by 66 mm bore and stroke

Type 37
Year 1929
Engine- 1.5 L (1496 cc/91 in³) straight-4
Power- n SOHC three-valve design and produced 60 hp (44 kW).
Type 37 A
Year 1929
Engine- 1.5 L (1496 cc/91 in³) straight-4
Power- n SOHC three-valve design and produced 80 hp (60kW).
Feature- shrouded brake drums.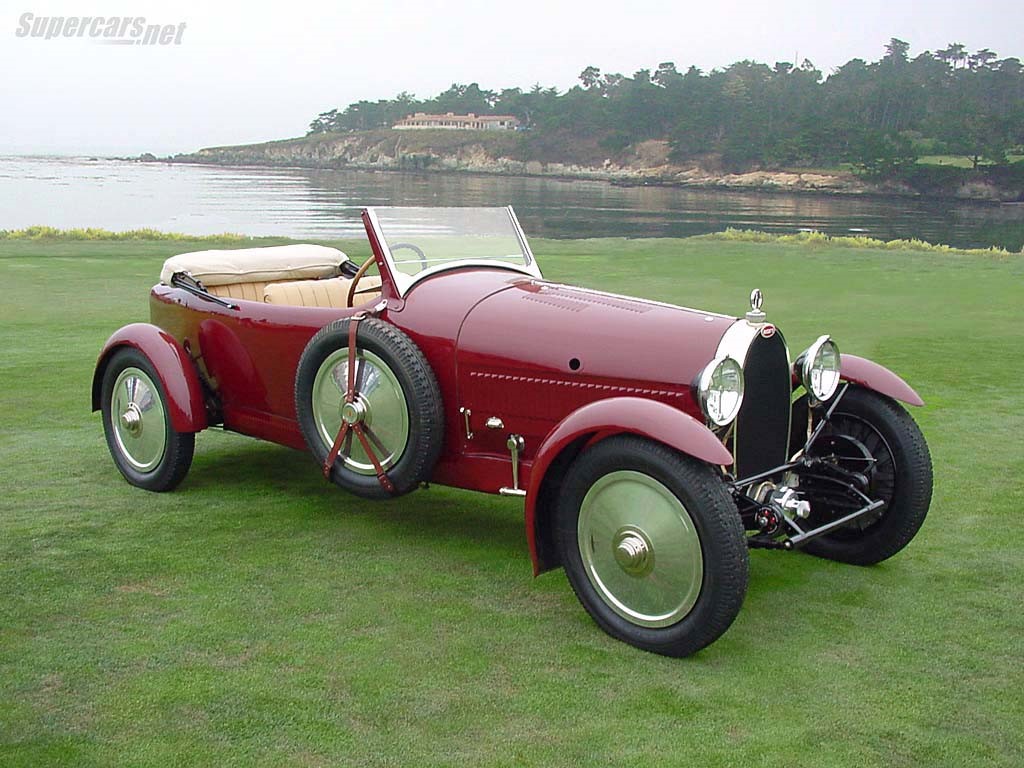
Type 38/ 38A
Year-1926 and 1927
Engine- 2 L (1991 cc/121 in³)

Type 39
Year 1931
Engine- 1.5 L (1493 cc/91 in³) with a shorter-stroked crankshaft, 66 mm,
Type 40
Engine- 2-litre MG type QPHG engine
Year-1929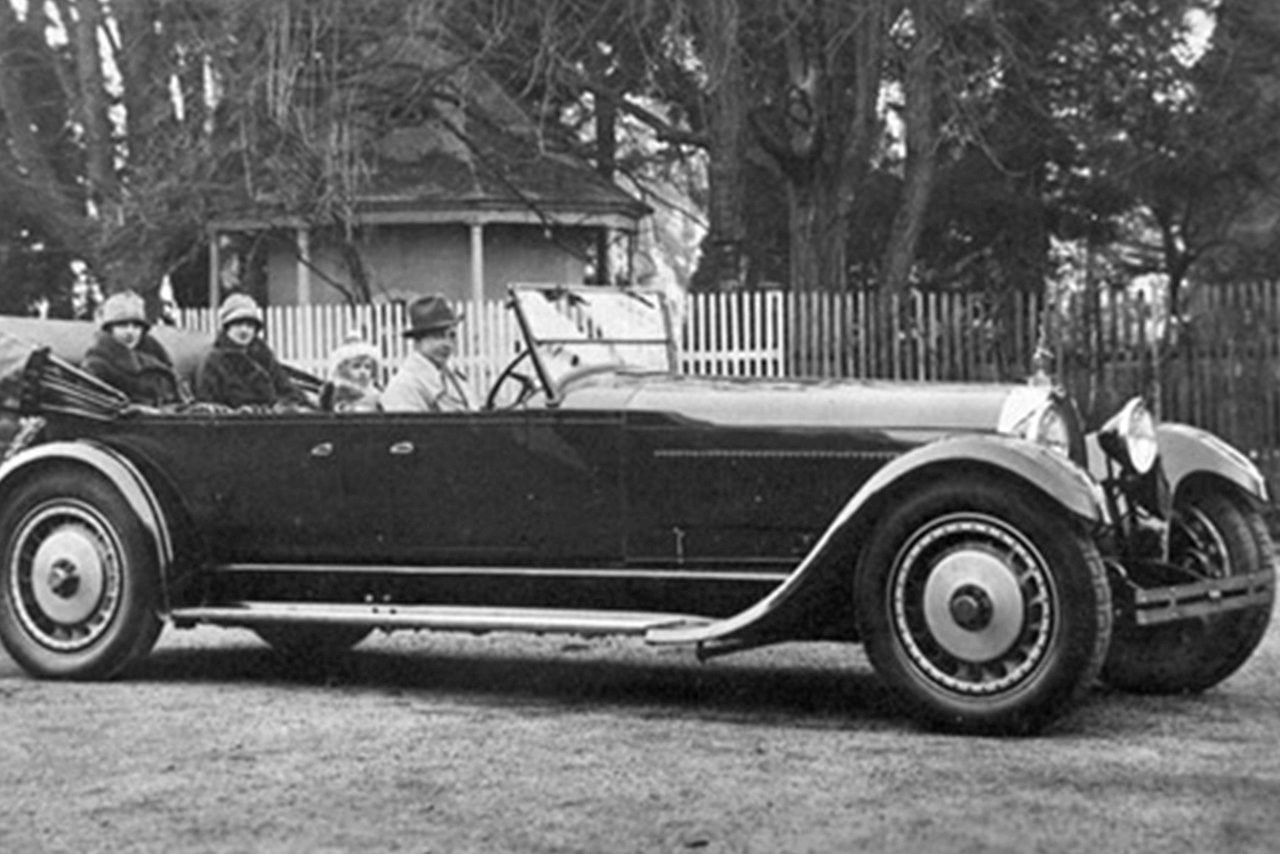
Type 41 {ROYALE}
Year 1926-1933
Powertrain
Engine 12,763 cc (12.7 L) (779 cu in.).straight-8
Transmission 3-speed manual
(7 produced, 6 existing; Ettore Bugatti wrecked the 7th)
Body and chassis
Class Luxury car, Classic car
Body style Berline, coupé, cabriolet, roadster
Layout FR layout
Dimensions
Wheelbase ~4.3 m (169.3 in)

Type 45
engine U16
position Front Longitudinal
aspiration Twin Roots Superchargers
valvetrain SOHC, 3 Valves per Cyl
fuel feed Twin Zenith Carburettors
displacement 3801 cc / 232.0 in³
bore 60 mm / 2.36 in
stroke 84 mm / 3.31 in
power 186.4 kw / 250 bhp
specific output 62.78 bhp per litre
bhp/weight 277.78 bhp per tonne
redline 5000
driven wheels Spur Driven RWD
wheel type Cast Aluminum GP
front tires 5.00 x 19
rear tires 5.00 x 19
front brakes Drums, Cable Operated
f brake size mm / in
rear brakes Drums, Cable Operated
r brake size mm / in
curb weight 900 kg / 1984 lbs
wheelbase 2596 mm / 102.2 in
front track 1250 mm / 49.2 in
rear track 1250 mm / 49.2 in
transmission 4-Speed Manual
gear ratios :1
final drive 2.80:1
Type 56
EngineElectric Motor
Power1 HP
TransmissionNone
0-60 TimeImpossible
Top Speed20 MPH
DrivetrainElectric
Engine PlacementRear
Curb Weight770 LBS
Seating2, Maybe 3
CargoProbably Not
MPGExcellent -height
Type 49
Year 1930-1934
Engine – ohc I-8 3,257 cc (199 cid) NA
1930-1934
Specifications of the 1930-1934 Bugatti Type 49:
Wheelbase, inches: 127.0
Length, inches: 165.0
Weight, pounds: Approximately 3,000

Type 50
Year 1930-1934
Engine – dohc I-8 4,972 cc (303.5 cid)
200hp
Wheelbase, inches: 122/138
Length, inches: 178.0+
Weight, pounds: 4,000+
Type 51
Engine- supercharged 2.3 L (2262 cc/138 in³) single overhead cam straight-8
160hp
Features- twin fuel caps behind the driver and finally the magneto being off-set to the left on the dash
Type 54
Engine- twin overhead-cam 4.9 liter engine delivering 300 hp (223 kW).

Type 54
Engine- twin overhead-cam 4.9 liter engine delivering 300 hp (223 kW).
Type 57
Production 1934–1940
710 produced
Body and chassis
Class Grand tourer
Powertrain
Engine 3,257 cc DOHC Inline 8
Type 57 T
Engine 3,257 cc DOHC Inline 8
185 kilometres per hour (115 mph).
Type 59
Engine- 3.3 L (3257 cc/198 in³) version of the straight-eight
Power-250hp
Features- piano wire wheels used splines between the brake drum and rim, and relied on the radial spokes to handle cornering loads. entTime
Type 57 C
Year – 1937
Engine-3.3 L engine from the road-going Type
Power-160 hp (119 kW)
Type 57SC gangloff
Year-1937
Engine-3.3 L engine from the road-going Type ( supercharged)
Power- 200 hp (150 kW) and 190 km/h (120 mph)
Wheelbase: 2,979 mm (117 in)
Track: 1,349 mm (53 in)
Weight: 950 kg (2,090 lb)
Type 57s/sc (altaltic)
Year-1935

Type 59 gp
Year-1933
Engine- 3.3l,
Wight- 750kg
Type 64
4.4 L (4432 cc/270 in³) 2-valve DOHC straight-8 engine
Year-1939
Body-Atlantic-style coupe, with gull-wing doors, designed
Designer-Jean Bugatti., Dimesion-130 in (3300 mm) wheelbase
Type 68
Year-1942
Engine-369cc 4-cylinder compressed engine, 4valves per cylinder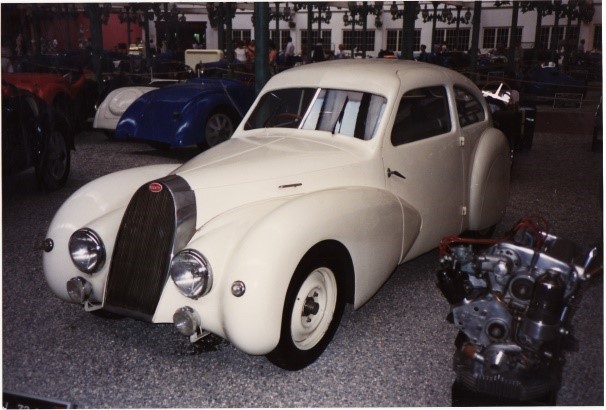
Type 73
Engine-4.7lt
Chassis-racing chassis ,ultra-low build,
Type 73c
Year-1947
Engine-1.5 L (1488 cc/90 in³) straight-4 engine, 4 valves per cylinder, a twin overhead camshaft, 76 mm bore and 95 mm stroke, wet cylinder liners, a detachable cylinder head, and a single cast iron exhaust manifold.
Type 101
Production 1951-1965
Engine 3,257 cc (3.257 L; 198.8 cu in) straight-8 Transmission 4-speed manual
Body and chassis
Class Grand tourer Body style 4-door saloon Cabriolet 2-door coach Coupé roadster
Layout FR layout
Wheelbase 3.3 m (130 in)[1]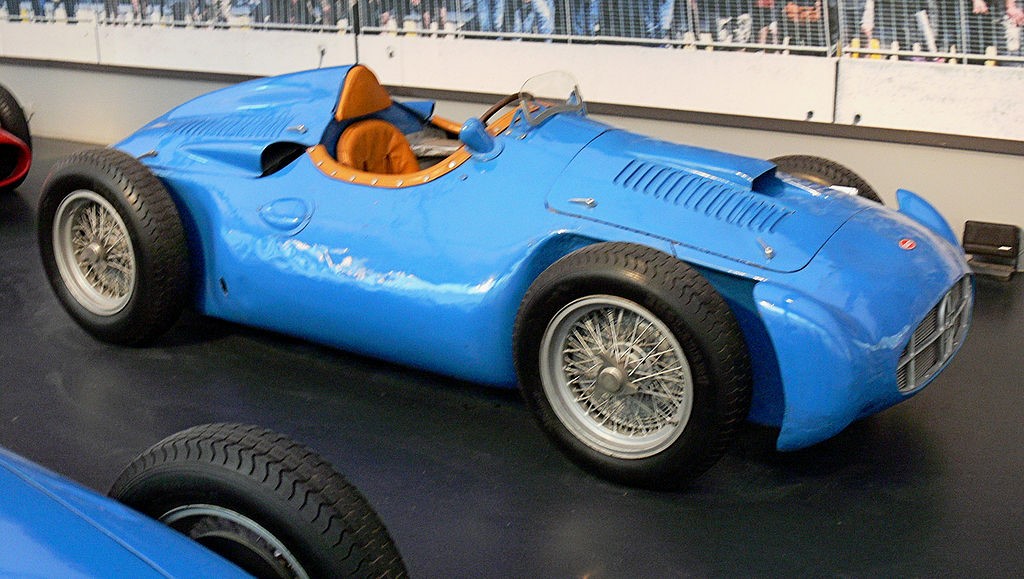
Bugatti type 251(final resurgence of authentic Bugatti)
Engine- 2.5 L (2486 cc/151 in³) straight-8. mounted transversely, behind the driver, over square engine with a 76 mm bore and 68.5 mm stroke
Year-1955.
Designed- Gioacchino Colombo Uniquely,.
Chassis- A de Dion tube rear suspension, racing chassis –
Bugatti type 252 (new era)
Powertrain
Engine 1.5 L Inline four, twin overhead camshafts
Designer Giovanni Michelotti
Body and chassis- MacPherson strut suspension in the front
Body style 2-door convertible
Layout FR layout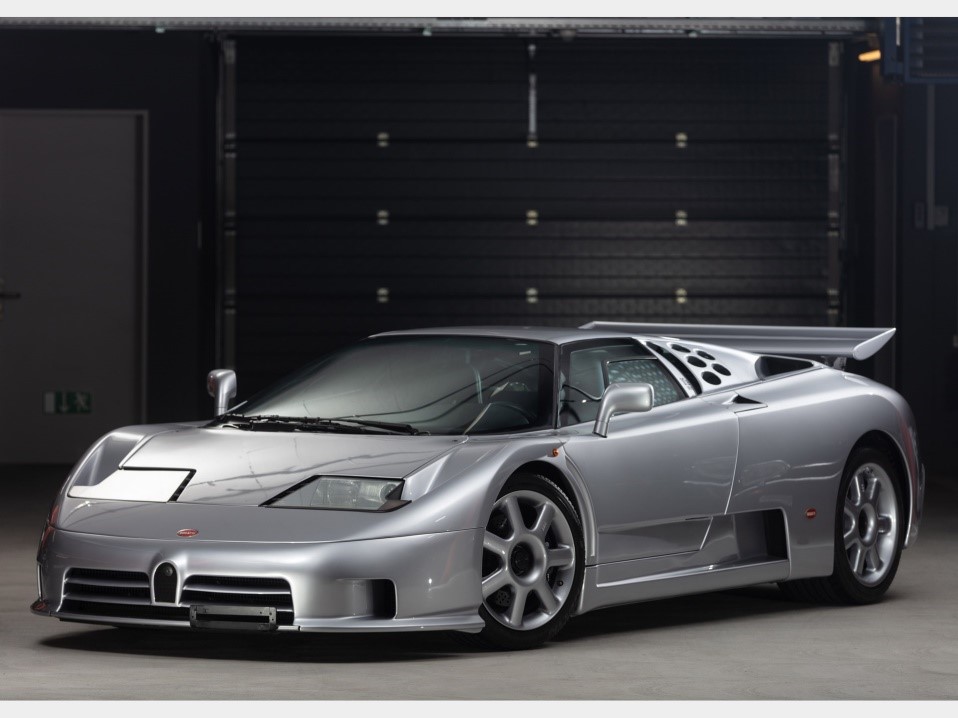
Bugatti EB110 (THE BEST SUPER CAR EVER BUILT)
Powertrain
Engine 3.5 L quad-turbocharged V12
Power output
GT: 412 kW (560 PS; 553 hp)
Super Sport: 450 kW (612 PS; 603 hp)
Transmission 6-speed manual
Production 1991–1995 (139 produced)
Assembly Italy: Modena, Campogalliano
Designer Marcello Gandini (prototypes) Giampaolo Benedini (final design)
Class Sports car (S)
Body style 2-door coupé
Layout Rear mid-engine, all-wheel drive
Doors Scissor
Related B Engineering Edonis
Bugatti EB 112
Wheelbase 2,550 mm (100.4 in) Length 4,400 mm (173.2 in) Width 1,940 mm (76.4 in) Height 1,114–1,125 mm (43.9–44.3 in)[1][2] Kerb weight 1,620 kg (3,571 lb), 1,418 kg (3,126 lb) Super Sport[3]
TEST RESULTS EB110
· 0–30 mph (48 km/h): 2.2 seconds
· 0–40 mph (64 km/h): 2.7 seconds
· 0–50 mph (80 km/h): 3.4 seconds
· 0–60 mph (97 km/h): 4.4 seconds
· 0–70 mph (113 km/h): 5.3 seconds
· 0–80 mph (129 km/h): 6.8 seconds
· 0–90 mph (145 km/h): 7.8 seconds
· 0–100 mph (161 km/h): 9.1 seconds
· 0–110 mph (177 km/h): 10.9 seconds
· 0–120 mph (193 km/h): 12.6 seconds
· Standing 1⁄4 mile (402 m): 12.5 seconds at 119.5 mph (192.3 km/h)
· Braking 60-0 mph: 112 ft
· Braking 80-0 mph: 209 ft
EB 112
Powertrain
Engine 6.0 L V12
Transmission 6-speed manual
Production
1993 (first prototype) 1998 (later examples)[1]
Assembly
Modena, Italy (first prototype) Monaco, Western Europe (later examples)
Designer Giorgetto Giugiaro (Italdesign)
Class Full-size luxury car (F) Body style 4-door fastback saloon, Layout Front-engine all-wheel-drive
Dimensions Wheelbase 3,100 mm (122.0 in) Length 5,070 mm (199.6 in) Width 1,960 mm (77.2 in) Height 1,405 mm (55.3 in) Kerb weight 1,800 kg (3,968 lb)
EB 118
Powertrain
Engine 6.3 L W18
Transmission 5-speed automatic
Production 1998
Designer Giorgetto Giugiaro (Italdesign)
Body and chassis
Class Concept car
Body style 2-door coupé
Layout Front-engine, all-wheel-drive
Dimensions
Length 198.8 in (5,050 mm)
Width 78.3 in (1,989 mm)
Height 55.9 in (1,420 mm)
Bugatti 18/3 chiron
Powertrain
Engine 6.3 L W18
Transmission 5-speed manual [1]
Production 1999
Assembly Moncalieri, Italy (Italdesign)
Designer Fabrizio Giugiaro at Italdesign Giugiaro under Hartmut Warkuß[1]
Body and chassis
Class concept car
Body style 2-door coupé Layout Mid-engine, four-wheel drive
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,650 mm (104 in) [2]
Length 4,420 mm (174 in)[2]
Width 1,994 mm (78.5 in)[2]
Height 1,150 mm (45 in)[2]
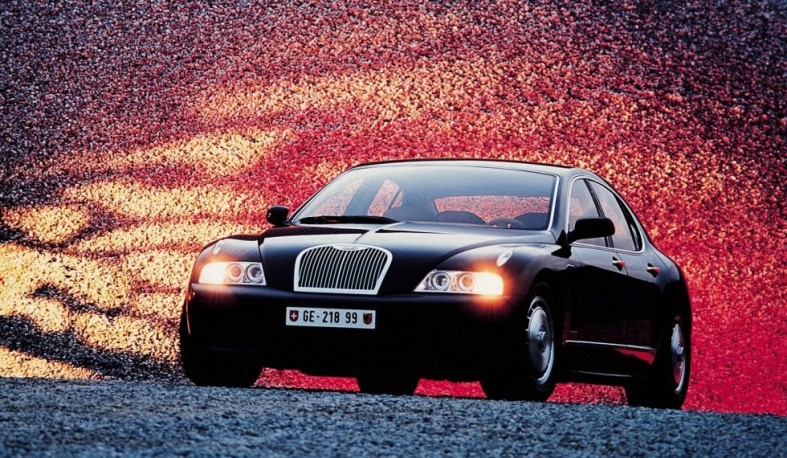

Eb 218
Lamborghini Diablo
Powertrain
Engine 6.3 litre, 72 Valve W18
Transmission 5-Speed automatic
Production 1999
Designer Giorgetto Giugiaro (Italdesign)
Body and chassis Class concept car Body style 4-door saloon
Layout Front-engine, all-wheel-drive
Dimensions
Wheelbase 3,000 mm (118.1 in)
Length 5,349 mm (210.6 in)
Width 1,989 mm (78.3 in)
Height 1,455 mm (57.3 in)
Curb weight 2,176.78 kg (4,799 lb)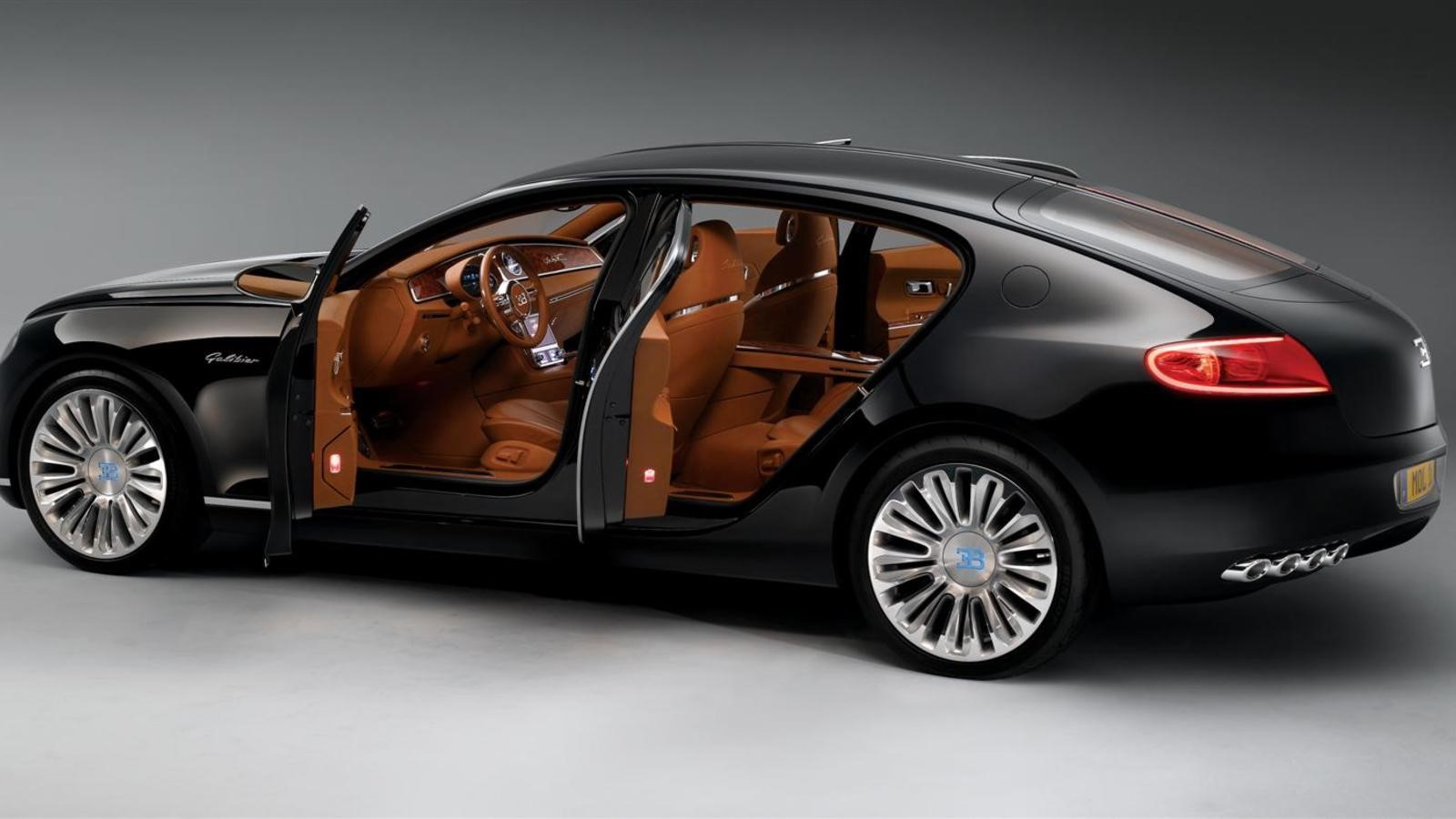
16-c galiber
Powertrain
Engine 8.0 L twin-supercharged W16
Transmission 8-speed automatic
Production 2009
Assembly Molsheim, Alsace, France
Body and chassis
Class Concept car
Body style 5-door fastback sedan
Layout Front-engine, all-wheel drive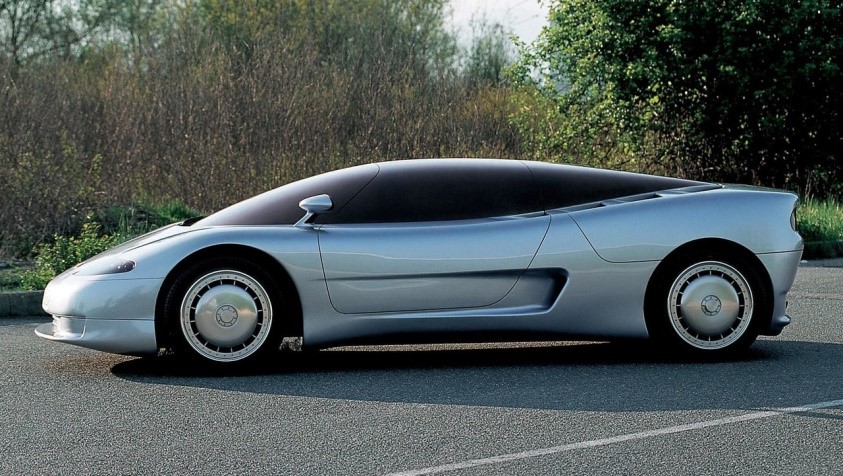
Bugatti id 90
Debuted: 1990 Turin Motor Show
Engine- mid-mounted 3.5-liter V12 engine with four turbochargers, all-wheel drive
Dimensions- 4.10 meters (161.4 inches) long, 1.84 meters (72.4 inches) wide.
Top speed- 174 mph (280 kph).
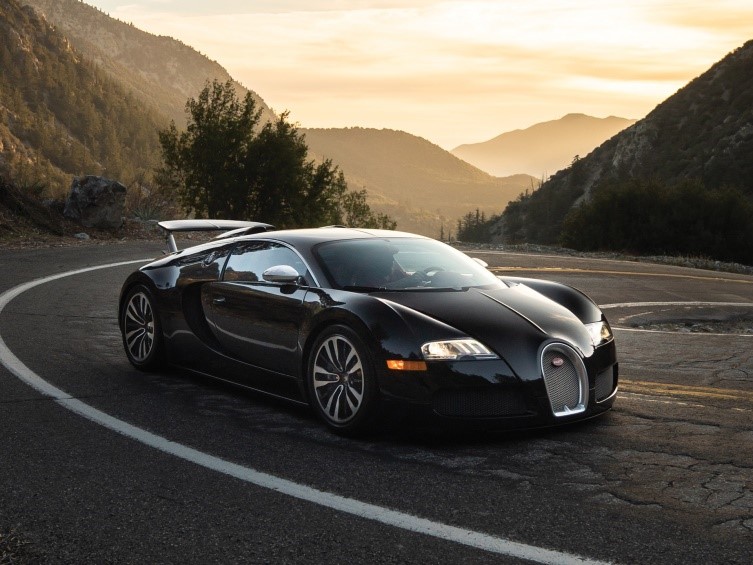

BUGATTI VEYRON 16.4
Engine 8.0 L (488 cu in) quad-turbocharged W16
Power output
Standard (Coupé), Grand Sport Roadster: 1,001 PS (987 hp; 736 kW)[2]
Super Sport (Coupé), Grand Sport Vitesse (Roadster): 1,200 PS (1,184 hp; 883 kW)[3][4]
Transmission 7-speed Direct Shift automatic
Specs – 3 heat exchangers for the air-to-liquid intercoolers.
3 engine radiators.
1 for the air conditioning system.
1 transmission oil radiator.
1 differential oil radiator.
1 engine oil radiator
Breaks- cross drilled, radially vented carbon fibre reinforced silicon carbide (C/SiC) composite discs,
The lightweight aluminium alloy monobloc brake calipers are made by AP Racing; the fronts have eight, titanium pistons and the rear calipers have six pistons.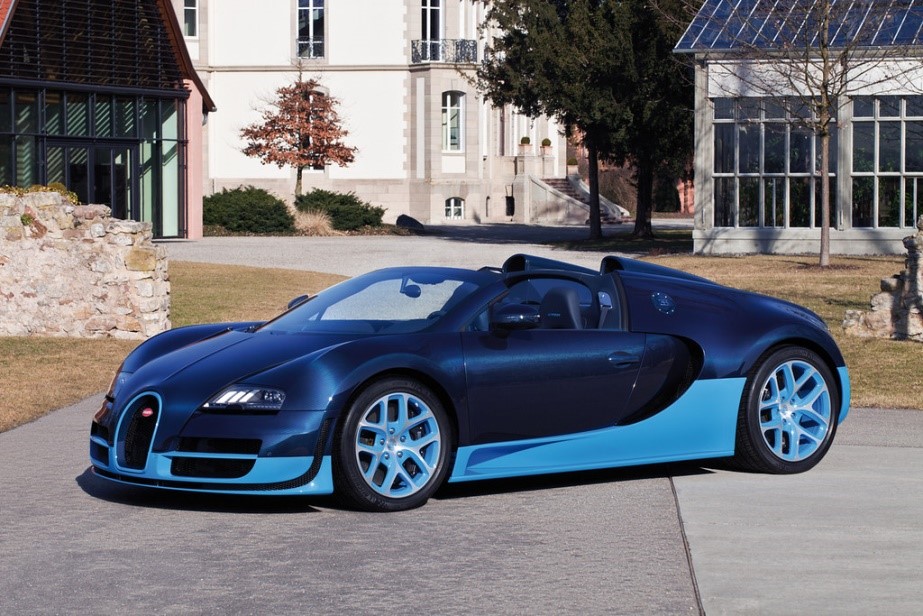
Production 2005–2011 (Veyron 16.4) 2009–2015 (Grand Sport) 2010–2011 (Super Sport) 2012–2015 (Grand Sport Vitesse)
Assembly France: Alsace, Molsheim
Designer Jozef Kabaň[1]
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Body style
2-door coupé (16.4, Super Sport)
2-door targa top (Grand Sport, Grand Sport Vitesse)
Layout Mid-engine, all-wheel drive
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,710 mm (106.7 in)
Length 4,462 mm (175.7 in)
Width 1,998 mm (78.7 in)
Height 1,159 mm (45.6 in)
Kerb weight 1,838–1,990 kg (4,052–4,387 lb)
Bugatti Veyron 16.4 super sport
Engine- engine power output of 1,200 PS (883 kW; 1,184 hp) at 6,400 rpm
torque of 1,500 N⋅m (1,106 lb⋅ft) at 3,000–5,000 rpm and a
revised aerodynamic package. a maximum torque of 1,500 Nm,
Acceleration- from 0 to 100 km/h in 2.5 seconds
top speed- 415 km/h – these were the performance specs that amazed and inspired experts and car fans throughout the world when this supercar was launched in 2010.
world speed record for road cars of 431.072 km/h.

BUGATTI CHIRON
Powertrain
Engine 8.0 L (488 cu in) quad-turbocharged W16
Power output 1,103 kW (1,500 PS; 1,479 hp)
Transmission 7-speed dual-clutch[2]
Top speed 465 km/h (289 mph)
Production 2016–present (Limited to 500) 2018–present (Chiron Sport)
Assembly France: Molsheim
Designer Achim Anscheidt (Head of Design, Sasha Selipanov Etienne Salome, Frank Heyl
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Body style 2-door coupé
Layout Mid-engine, all-wheel-drive
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,711 mm (106.7 in)
Length 4,544 mm (178.9 in)[3]
Width 2,038 mm (80.2 in)
Height 1,212 mm (47.7 in)
Kerb weight
1,996 kg (4,400 lb) (est)[4]
1,978 kg (4,360 lb) (est) (Chiron Sport)
Bugatti chiron sports
Specs- identical to chiron
1,500 PS (1,479 hp; 1,103 kW) from a quad-turbocharged W16 engine but is 18 kg (40 lb) lighter due to the extensive use of carbon fibre and utilises a stiffer suspension in order to increase the cornering ability of the car while maintaining its grand touring characteristics.
10ans Bugatti
Specs- identical to chiron
February 2019, the 110 Ans Bugatti is a limited edition variant of the Chiron Sport developed to celebrate 110 years of Bugatti. The car features carbon fibre body work finished in matte Steel Blue exterior colour. The body is also accented with Steel Blue bare carbon fibre. The exhaust system of the car is finished in matte black colour.
The colours of the French flag are present on the wing mirrors, fuel filler cap and on the underside of the rear wing. The brake callipers are finished in blue colour. so-fon
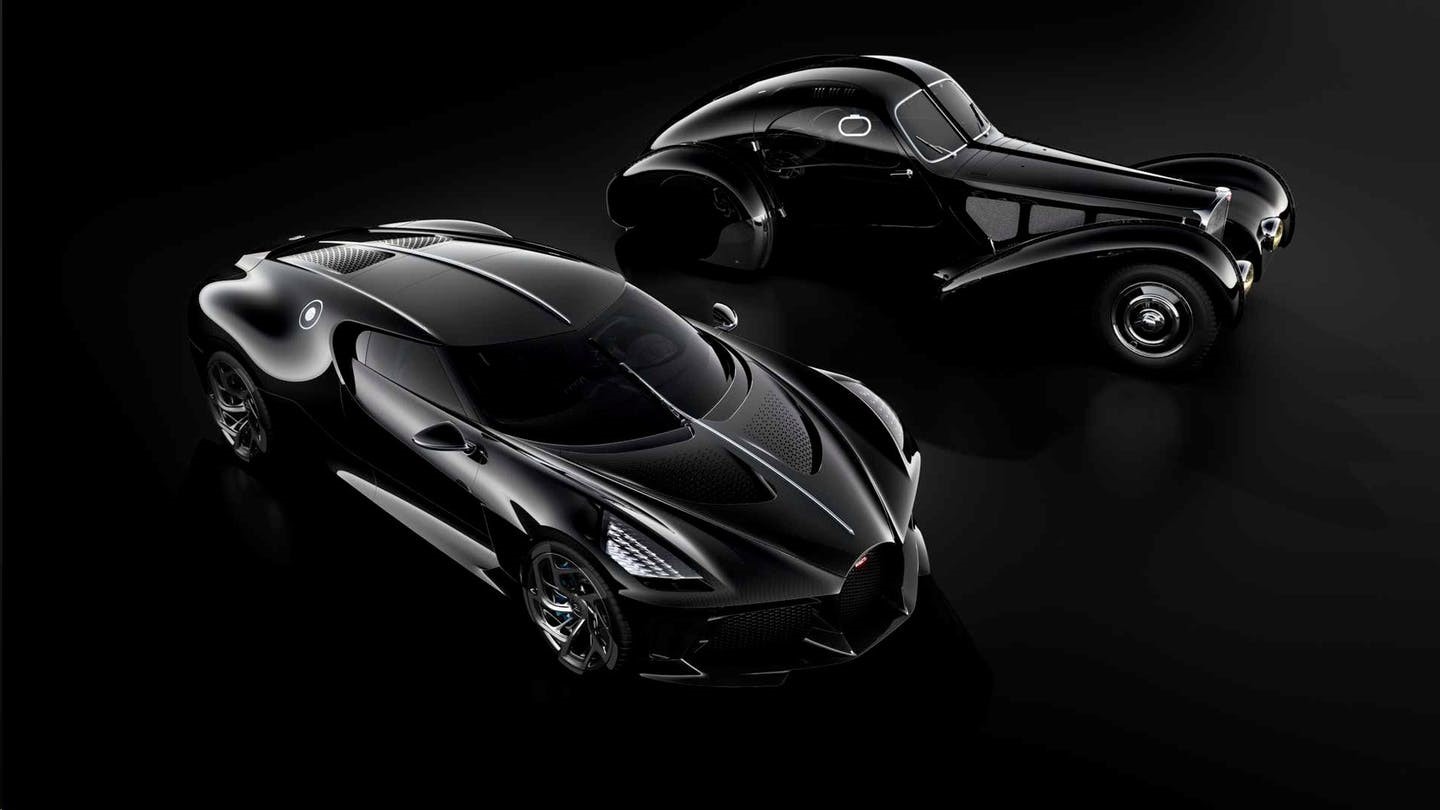

Bugatti la voiture noire
Specs identical to chiron
Bugatti divo
roduction 2018–present
(40 units planned)
Assembly France: Alsace, Molsheim
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Body style 2-door coupé
Layout Mid-engine, all-wheel-drive
Related Bugatti Chiron
Powertrain
Engine 8.0 L (488 cu in) quad-turbocharged W16
Power output 1,103 kW (1,500 PS; 1,479 hp)
Transmission 7-speed dual-clutch
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,711 mm (106.7 in)
Length 4,641 mm (182.7 in)
Width 2,018 mm (79.4 in)
Height 1,212 mm (47.7 in)
Kerb weight 1,961 kg (4,323 lb) (est)
FERRARI

125s
Powertrain
Engine 1.5 L (1496.77 cc) Colombo V12
Transmission 5-speed manual
Manufacturer Ferrari
Production 1947
2 produced
Designer Gioacchino Colombo/Scuderia Ferrari
Body and chassis
Class Sports car
Layout FR layout
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,420 mm (95.3 in)
Curb weight 650 kg (1,433 lb)
159s
Powertrain
Engine 1.9 L (1902.84 cc) Colombo V12
Transmission 5-speed manual
Manufacturer Ferrari
Production 1947
2 produced
Designer Gioacchino Colombo
Body and chassis
Class Sports car
Layout FR layout
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,420 mm (95.3 in)
Curb weight 750 kg (1,653 lb)
166s/mm
Powertrain
Engine 2.0 L (1995.02 cc) Colombo V12
Transmission 5-speed manual
Manufacturer Ferrari
Production 1948 – 1953
3 (Sport)
9 (Spyder Corsa)
47 (MM)[1]
Designer Carlo Anderloni at Carrozzeria Touring[2], Carrozzeria Allemano
Body and chassis
Class Sports car
Body style Berlinetta
Spider
Layout FR layout
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,420 mm (95 in)
2,200 mm (87 in) (MM)
Curb weight 800 kg (1,764 lb) (S, berlinetta)
650 kg (1,433 lb) (MM, spider)

166 inter
Powertrain
Engine 2.0 L (1995.02 cc) Colombo V12
Transmission 5-speed manual
Production 1948 – 1950
38 produced
Designer Carlo Anderloni at Carrozzeria Touring, Carrozzeria Vignale
Body and chassis
Class Grand tourer
Body style Coupé
Layout FR layout
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,620 mm (103 in)
Curb weight 900 kg (1,984 lb) (coupé)
195 inter
Powertrain
Engine 2.3 L (2341.02 cc) Colombo V12
Transmission 5-speed manual
Production 1950-1951
28 produced
Body and chassis
Class Grand tourer
Layout FR layout
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,500 mm (98 in)
Curb weight 950 kg (2,094 lb) (coupé)
195 s
Powertrain
Engine 2.3 L (2341.02 cc) Colombo V12
Transmission 5-speed manual
Production 1950
4 converted from 166 MM[1]
Designer Carrozzeria Touring[2]
Body and chassis
Class Sports car
Body style Berlinetta
Barchetta
Layout FR layout
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,250 mm (89 in)
Curb weight 720 kg (1,587 lb) (barchetta)

212 export
Powertrain
Engine 2.6 L (2562.51 cc) Colombo V12
Transmission 5-speed manual
Production 1951
27 produced
Body and chassis
Class Sports car
Body style Berlinetta
Barchetta
Layout FR layout
Related Ferrari 212 Inter
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,250 mm (88.6 in)
Curb weight 850 kg (1,874 lb) (berlinetta)
212 inter
Powertrain
Engine 2.6 L (2562.51 cc) Colombo V12
Transmission 5-speed manual
Production 1951–1952
82 produced
Designer Carrozzeria Touring,[1] Pinin Farina, Vignale, Ghia, Stabilimenti Farina
Body and chassis
Class Sports car
Layout FR layout
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,600 mm (102 in)
Curb weight 1,000 kg (2,205 lb) (coupé)
340 america
Powertrain
Engine 4.1 L (4101.66 cc) Lampredi V12
Power output 220 PS
Transmission 5-speed manual
Production 1950–1952
23 made (two were converted from 275 S)
Body and chassis
Body style 2-door coupé
2-door roadster
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,420 mm (95.3 in)
Kerb weight 900 kg (1,984 lb) (dry, berlinetta )
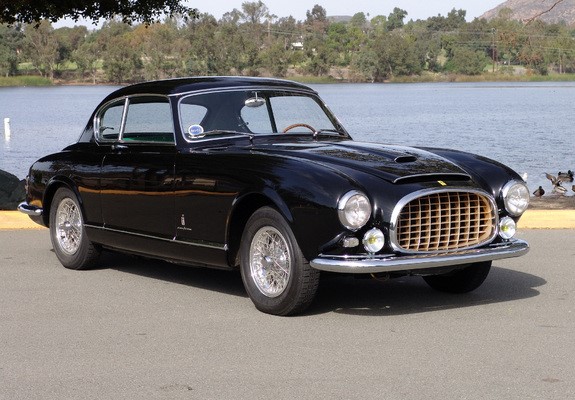

342 america
Powertrain
Engine 4.1 L (4101.66 cc) Lampredi V12
Power output 200 PS
Transmission 4-speed manual
Production 1952
6 made
Body and chassis
Body style 2-door coupé
2-door convertible
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,650 mm (104.3 in)
Kerb weight 1,200 kg (2,646 lb)
375 america
Powertrain
Engine 4.5 L (4522.08 cc) Tipo 104 Lampredi V12
Power output 300 PS
Transmission 4-speed manual
Production 1953–1954
12 made (two were converted from 250 Europas)
Body and chassis
Body style 2-door coupé
2-door roadster
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,800 mm (110.2 in)
Kerb weight 1,150 kg (2,535 lb)
410 super americana
Powertrain
Engine 5.0 L (4962.96 cc) Tipo 126 Lampredi V12
Power output 340 PS/360 PS
Transmission 4-speed manual
Production 1955–1959
35 made
Body and chassis
Body style 2-door coupé
2-door roadster
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,800 mm (110.2 in)
2,600 mm (102.4 in)
Kerb weight 1,200 kg (2,646 lb)

F400 super Americana
Powertrain
Engine 4.0 L (3967.44 cc) Tipo 163 Colombo V12
Power output 340 PS
Transmission 4-speed manual with overdrive
Production 1959—1964
47 made
Designer Aldo Brovarone at Pinin Farina (Coupé Aerodinamico)
Body and chassis
Body style 2-door coupé
2-door roadster
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,420 mm (95.3 in)(series I)
2,600 mm (102.4 in)(series II)
Kerb weight 1,250 kg (2,756 lb) (dry, coupé)
F 500 superfast
Powertrain
Engine 5.0 L (4962.96 cc) Tipo 208 Colombo V12
Power output 400 PS
Transmission 4-speed manual with overdrive
5-speed manual
Production 1964–1966
36 made
Designer Pininfarina
Body and chassis
Body style 2-door coupé
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,650 mm (104.3 in)
Length 4,820 mm (189.8 in)
Width 1,730 mm (68.1 in)
Height 1,280 mm (50.4 in)
Kerb weight 1,400 kg (3,086 lb)
F 365 California
Powertrain
Engine 4.4 L (4390.35 cc) Tipo 217B Colombo V12
Power output 320 PS
Transmission 5-speed manual
Production 1966–1967
14 made
Designer Tom Tjaarda at Pininfarina[13]
Body and chassis
Body style 2+2 convertible
Related Ferrari 500 Superfast
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,650 mm (104.3 in)
Length 4,900 mm (192.9 in)
Width 1,780 mm (70.1 in)
Height 1,330 mm (52.4 in)
Kerb weight 1,320 kg (2,910 lb)

F 250 europa/ gt
Layout Longitudinally-mounted, front-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Powertrain
Engine 3.0 L (2953.21 cc) Colombo V12
3.0 L (2963.45 cc) Lampredi V12 (Europa)
Transmission 4-speed manual
5-speed manual
Production 1953–1964
Designer Giotto Bizzarrini
Sergio Scaglietti
Pinin Farina
Vignale
Ghia
Body and chassis
Class Grand Tourer
Body style Berlinetta
cabriolet
coupé
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,400 mm (94.5 in) (SWB)
2,600 mm (102.4 in) (LWB)
2,800 mm (110.2 in) (Europa)
F 330 TRI/LM spyder 0808
Engine Tipo 163 3,967 cc (242.1 cu in) V12 naturally-aspirated front-engine, longitudinally mounted
Transmission Tipo 568 5-speed manual transmission
Designer(s) Medardo Fantuzzi
Technical specifications
Chassis tubular steel spaceframe
Suspension (front) Coil spring and independent wishbone
Suspension (rear) Coil spring and independent wishbone
Length 178 in (452.1 cm)
Width 62.6 in (159.0 cm)
Height 41.3 in (104.9 cm)
Axle track F: 56 in (142.2 cm)
R: 55.7 in (141.5 cm)
Wheelbase 94.5 in (2,400.3 mm)
Weight 820 kg (1,807.8 lb)
Tyres F: 6.00 x 16
R: 7.00 x 16
275
GTB,
Production
1964–1966 (275 GTB, GTS)
1966–1968 (275 GTB/4)
Powertrain
Engine
3.3 L Colombo V12 engine
with two overhead camshafts (275 GTB, GTB/C and GTS)
or four overhead camshafts (275 GTB/4 and GTS/4 NART Spyder)
Transmission 5-speed manual transaxle with synchromesh
1967 (275 GTS/4 NART Spyder)
Designer
Pininfarina
Scaglietti (275 GTS/4 NART Spyder)
Body and chassis
Class Grand tourer
Body style
2-door coupé (GTB models)
2-door spider (GTS models)
Layout Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,400 mm (94.5 in)
Curb weight
1,300 kg (2,866 lb) (steel bodied 275 GTB/4)
1,112 kg (2,452 lb) (alloy-bodied 275 GTB/C)
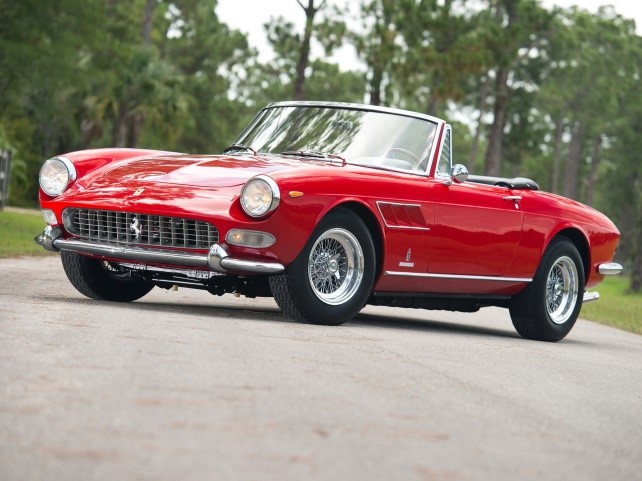

Production
1964–1966 (275 GTB, GTS)
1966–1968 (275 GTB/4)
Powertrain
Engine
3.3 L Colombo V12 engine
with two overhead camshafts (275 GTB, GTB/C and GTS)
or four overhead camshafts (275 GTB/4 and GTS/4 NART Spyder)
Transmission 5-speed manual transaxle with synchromesh
1967 (275 GTS/4 NART Spyder)
Designer
Pininfarina
Scaglietti (275 GTS/4 NART Spyder)
Body and chassis
Class Grand tourer
Body style
2-door coupé (GTB models)
2-door spider (GTS models)
Layout Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,400 mm (94.5 in)
Curb weight
1,300 kg (2,866 lb) (steel bodied 275 GTB/4)
1,112 kg (2,452 lb) (alloy-bodied 275 GTB/C)
Production
1964–1966 (275 GTB, GTS)
1966–1968 (275 GTB/4)
Powertrain
Engine
3.3 L Colombo V12 engine
with two overhead camshafts (275 GTB, GTB/C and GTS)
or four overhead camshafts (275 GTB/4 and GTS/4 NART Spyder)
Transmission 5-speed manual transaxle with synchromesh
1967 (275 GTS/4 NART Spyder)
Designer
Pininfarina
Scaglietti (275 GTS/4 NART Spyder)
Body and chassis
Class Grand tourer
Body style
2-door coupé (GTB models)
2-door spider (GTS models)
Layout Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,400 mm (94.5 in)
Curb weight
1,300 kg (2,866 lb) (steel bodied 275 GTB/4)
1,112 kg (2,452 lb) (alloy-bodied 275 GTB/C)
Production
1964–1966 (275 GTB, GTS)
1966–1968 (275 GTB/4)
Powertrain
Engine
3.3 L Colombo V12 engine
with two overhead camshafts (275 GTB, GTB/C and GTS)
or four overhead camshafts (275 GTB/4 and GTS/4 NART Spyder)
Transmission 5-speed manual transaxle with synchromesh
1967 (275 GTS/4 NART Spyder)
Designer
Pininfarina
Scaglietti (275 GTS/4 NART Spyder)
Body and chassis
Class Grand tourer
Body style
2-door coupé (GTB models)
2-door spider (GTS models)
Layout Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,400 mm (94.5 in)
Curb weight
1,300 kg (2,866 lb) (steel bodied 275 GTB/4)
1,112 kg (2,452 lb) (alloy-bodied 275 GTB/C)

DINO206 GT
Production 1968–1969 (152 produced)
Designer Leonardo Fioravanti at Pininfarina
Powertrain
Engine 2.0 L V6
Transmission 5-speed manual
DINO 246 GT/GTS
Production 1969–1974
Powertrain
Engine 2.4 L V6
Transmission 5-speed manual
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,280 mm (90 in)[1]
Length 4,150 mm (163 in)[1]
Width 1,700 mm (67 in)[1]
Height 1,115 mm (44 in)[1]
Kerb weight 900 kg (1,984.2 lb)
DINO 308 GT4 2+2
Production 1973–1976
(branded as Dino)
1976–1980
(branded as Ferrari)
Designer Marcello Gandini at Bertone
Body and chassis
Body style 2+2 coupé
Powertrain
Engine 3.0 L V8
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,340 mm (92 in)[6]
Length 4,235 mm (167 in)[6]
Width 1,700 mm (67 in)[6]
Height 1,135 mm (45 in)[6]
Kerb weight 1,080 kg (2,381.0 lb)

308 GTB
Manufacturer Ferrari
Production 1975–1985
Assembly Maranello, Italy
Designer Leonardo Fioravanti at Pininfarina[1]
Body and chassis
Class Sports car
Body style Berlinetta (GTB)
Targa top (GTS)
Layout Transverse mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Related Ferrari 208/308 GT4
Ferrari Mondial
Ferrari 288 GTO
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,340 mm (92.1 in)
Length 4,230 mm (166.5 in)
Width 1,720 mm (67.7 in)
Height 1,120 mm (44.1 in)
308 GTS/ GTB, GTBI/GTBS
Production 1975–1980 (GTB)
1977–1980 (GTS)
1980–1983 (GTBi/GTSi)
Powertrain
Engine 2.9 L Tipo F106 AB V8 (GTB/GTS)
2.9 L Tipo F106 BB V8 (GTBi/GTSi)
Transmission 5-speed manual[2]
Dimensions
Kerb weight 1,090 kg (2,403 lb) (GTB)
1,286 kg (2,835 lb) (GTBi)
308 QUATRAVALVOLLE
Production 1982–1985
Engine 2.9 L (2,927 cc) Tipo F105 AB V8
Transmission 5-speed manual
Kerb weight 1,465 kg (3,230 lb)

208GTB/ 208GTS
Production 1980–1981
Engine 2.0 L Tipo F106 CB 000 V8
208 GTS/GTB TURBO
Production 1982–1985
Engine 2.0 L Tipo F106 D 000 turbocharged V8
F GTB/GTS TURBO
Powertrain
Engine 2.0 L Tipo F106 N turbocharged V8
Transmission 5-speed manual
Production 1986–1989
Body and chassis
Body style Berlinetta Targa
Layout Transverse rear mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Kerb weight 1,265–1,275 kg (2,789–2,811 lb)

328 GTB/GTS
Powertrain
Engine 3.2 L Tipo F105CB V8
Transmission 5-speed manual
Production 1985-1989
Model years 1986-1989
Assembly Maranello, Italy
Designer Leonardo Fioravanti at Pininfarina
Body and chassis
Class Sports car
Body style Berlinetta Targa
Layout Transverse, rear mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Related Ferrari 3.2 Mondial
Ferrari 208 GTB & GTS
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,350 mm (92.5 in)
Length 4,255 mm (167.5 in)
Width 1,730 mm (68.1 in)
Height 1,128 mm (44.4 in)
Curb weight 1,263 kg (2,784 lb)
F348
Powertrain
Engine 3.4 L Tipo F119 V8
Transmission 5-speed manual[2]
Production 1989–1995
8,844 produced
Assembly Maranello, Italy
Designer Leonardo Fioravanti at Pininfarina [1]
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Body style 2-door Berlinetta (TB, GTB) 2-door targa top (TS, GTS) 2-door convertible
Layout Longitudinal, rear mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Related Ferrari Mondial T
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,450 mm (96.5 in)[2]
Length 4,230 mm (167 in)[2]
Width 1,894 mm (74.6 in)[2]
Height 1,170 mm (46.1 in)[2]
Kerb weight 1,500 kg (3,300 lb) 84 lb)
348TB/TS Engine:
(F119D, F119G) DOHC, 32 Valve V8, 3405 cc / 207.77 cid
Bore/Stroke: 85mm x 75mm
Compression ratio: 10.4:1
Power: 300 PS (221 kW; 296 hp) at 7,200 rpm
Maximum Torque: 238 lb/ft, 324 Nm at 4,200 rpm
Transmission: 5-speed manual
Chassis: Steel platform & sub-frame
Suspension: Independent all round
Brakes: 4-wheel Disc ABS
Max. Speed: 267 km/h (166 mph)[3]
Acceleration:
0–97 km/h (60 mph): 6.0 s[3]
0–161 km/h (100 mph): 15.3 s[3]
1/4 mile : 14.5 s[3]

CHALLENGE
F348 GTB GTS SPIDER
Engine:(F119H) DOHC, 32 Valve V8, 3405 cc
Bore/Stroke: 85mm x 75mm
Compression ratio: 10.8:1
Power: 320 PS (235 kW; 316 hp) @ 7,200 rpm
Maximum Torque: 238 lb/ft, 324 Nm @ 5,000 rpm
Transmission: 5-speed manual
Chassis: Steel platform & sub-frame
Suspension: Independent all round
Brakes: 4-wheel Disc ABS
Max. Speed: over 280 km/h (over 174 mph)[8]
Acceleration
0–100 km/h (62 mph): 5.4 s
0–161 km/h (100 mph): 12.0 s
1/4 mile : 13.6 s (As rated)
spider
F348 GTB GTS SPIDER
Engine:(F119H) DOHC, 32 Valve V8, 3405 cc
Bore/Stroke: 85mm x 75mm
Compression ratio: 10.8:1
Power: 320 PS (235 kW; 316 hp) @ 7,200 rpm
Maximum Torque: 238 lb/ft, 324 Nm @ 5,000 rpm
Transmission: 5-speed manual
Chassis: Steel platform & sub-frame
Suspension: Independent all round
Brakes: 4-wheel Disc ABS
Max. Speed: over 280 km/h (over 174 mph)[8]
Acceleration
0–100 km/h (62 mph): 5.4 s
0–161 km/h (100 mph): 12.0 s
1/4 mile : 13.6 s (As rated)
Powertrain
Engine 3.5 L 5V DOHC F129 B/C V8
Transmission
6-speed manual
6-speed ‘F1’ electrohydraulic manual
Manufacturer Ferrari
Production 1994–1999
11,273 produced
Model years 1995–1999
Assembly Maranello, Italy
Designer Pininfarina
Class Sports car (S)
Body style 2-door berlinetta
2-door targa top 2-door spider
Layout Longitudinal, Rear mid-engine, rear-wheel drive
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,451 mm (96.5 in)
Length 4,249 mm (167.3 in)
Width 1,900 mm (75 in)
Height 1,171 mm (46.1 in)
Curb weight 1,483–1,497 kg (3,270–3,300 lb)

F360
Powertrain
Engine 3.6 L (3,586 cc) Tipo F131 V8
Transmission 6-speed manual
6-speed ‘F1’ electrohydraulic manual
Production 1999–2004
8,800 (Modena) 7,565 (Spider)
1,288 (Challenge Stradale)[1]
Model years 2000–2004
Assembly Maranello, Italy
Designer Pininfarina
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Body style 2-door berlinetta
2-door spider Layout Longitudinal, Rear mid-engine, rear-wheel drive
Wheelbase 2,600 mm (102 in)
Length 4,477 mm (176 in)
Width 1,922 mm (76 in)
Height 1,214 mm (48 in) (Modena)
1,214 mm (48 in) (Spider)
Curb weight 1,493 kg (3,291 lb) (Modena)
1,553 kg (3,424 lb) (Spider)[3]
1,430 kg (3,152 lb) (Challenge Stradale)
Challenge stadale
Engine
Type: Naturally aspirated 90° V8 engine F131
Position: Longitudinally-mounted Rear mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout
Valvetrain: DOHC 5 valves per cylinder
Fuel feed: Bosch Motronic 7.3 fuel injection
Bore X stroke: 85 mm × 79 mm (3.35 in × 3.11 in)
Total displacement: 3,586 cc (3.6 L; 218.8 cu in)
Redline: 8,700 rpm
Compression ratio: 11.2:1
Max. power: 425 PS (419 hp; 313 kW) at 8,500 rpm
Max. torque: 373 N⋅m; 275 lbf⋅ft (38 kg⋅m) at 4,750 rpm[15]
Performance
0-97 km/h (60 mph): 4.0 seconds [16]
Top speed: Redline limited – 283 km/h (176 mph)[16]
Downforce: about 270 kgf (2.6 kN) at 300 km/h (190 mph) (without rear wing)
Lift to drag: about -1.1:1
Overall length: 4,477 mm (176.3 in)
Overall width: 1,922 mm (75.7 in)
Height: 1,199 mm (47.2 in)
Wheelbase: 2,600 mm (102.4 in)
Front track: 1,669 mm (65.7 in)
Rear track: 1,617 mm (63.7 in)
Dry weight: 1,180 kg (2,601 lb)
Curb weight: 1,430 kg (3,153 lb)
Fuel capacity: 95 L (25 US gal; 21 imp gal)
360modena challenge
Specs- all identical
Official Performance figures
Power (SAE net): 416 PS (306 kW; 410 hp) at 8,500 rpm
Torque (SAE net): 286 lb⋅ft (388 N⋅m) at 4,750 rpm
0–100 km/h (0–62 mph): 3.9 seconds
Top speed (limited): 298 km/h (185 mph)
Kerb Weight: 1,250 kg (2,756 lb)
Dry Weight: 1,169 kg (2,577 lb)

F 330 AMERICA
ENGINE- 4.0 L (3967.44 cc) Tipo 209 Colombo V12
Overview
Production 1963
50 produced
Designer Pininfarina
Body and chassis
Body style 2+2 Coupé
Related Ferrari 250 GT/E 2+2
330 GT 2+2
ENGINE- 4.0 L (3967.44 cc) Tipo 209 Colombo V12
Production 1964–1967
1,099 produced
Designer Tom Tjaarda at Pininfarina[2]
Body and chassis
Body style 2+2 Coupé
330 LMB
ENGINE- 390 hp (291 kW) at 7,500 rpm )

330P
ENGINE AND POWER- The 330 P4 had 450 hp at 8000 rpm, which combined with its low weight of 792 kg (1746,06 lb) resulted in a top speed of 320 km/h (198.85 mph)
330GTS/GTC
Overview
Production 1966–1968
GTC: 598 produced
GTS: 100 produced
Designer Pininfarina
Body and chassis
Body style GTC: 2-seat coupé
GTS: 2-seat Spider
365 GTS/GTC
365 GTS/GTC
Engine 4.4 L Tipo 245C Colombo V12[3]
Transmission 5-speed manual all-synchromesh[4]
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,400 mm (94.5 in)[3]
Length 4,470 mm (176.0 in)[3]
Width 1,670 mm (65.7 in)[3]
Height 1,300 mm (51.2 in)[3]
Kerb weight 1,350 kg (2,976 lb) (dry)[3]
Production 1968–1970
GTC: 168 produced
GTS: 20 produced
Body and chassis
Body style GTC: 2-seat coupé
GTS: 2-seat spider

F GTB/4 GTS/4
Powertrain
Engine 4.4 L (4390.35 cc) Tipo 251 Colombo V12
Transmission 5-speed manual
Production
GTB/4: 1968–1973
1,284 produced
GTS/4: 1971–1973
122 produced
Designer Leonardo Fioravanti at Pininfarina[1]
Body and chassis
Class Sports car
Body style
GTB/4: berlinetta
GTS/4: spider
Layout Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,400 mm (94.5 in)[2]
Length 4,425 mm (174.2 in)[2]
Width 1,760 mm (69.3 in)[2]
Height 1,245 mm (49.0 in)[2]
Kerb weight 1,200 kg (2,646 lb) (GTB/4, dry)
F GTB/4 GTS/4
Powertrain
Engine 4.4 L (4390.35 cc) Tipo 251 Colombo V12
Transmission 5-speed manual
Production
GTB/4: 1968–1973
1,284 produced
GTS/4: 1971–1973
122 produced
Designer Leonardo Fioravanti at Pininfarina[1]
Body and chassis
Class Sports car
Body style
GTB/4: berlinetta
GTS/4: spider
Layout Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,400 mm (94.5 in)[2]
Length 4,425 mm (174.2 in)[2]
Width 1,760 mm (69.3 in)[2]
Height 1,245 mm (49.0 in)[2]
Kerb weight 1,200 kg (2,646 lb) (GTB/4, dry)
BERLINETTA BOXER
Layout Rear mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Powertrain
Engine Flat-12
Transmission 5-speed manual
Production 1973–1984
2,323 produced
Assembly Maranello, Italy
Designer Leonardo Fioravanti at Pininfarina[1]
Body and chassis
Class Sports car
Body style 2-door berlinetta
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,500 mm (98.4 in)
Length 4,400 mm (173.2 in)
Width 1,830 mm (72.0 in)
Height 1,120 mm (44.1 in)

365 GT/4 BB
Production 1973–1976
387 produced
Powertrain: Engine 4.4 L F102A Flat-12 : 1
BB512
Production 1976–1981
929 produced
PowertrainEngine 4.9 L F102B F-12
BB512 I
Production 1981–1984
1,007 produced
Powertrain:Engine 4.9 L F110A FI F-12

TESTOROSSA F512 TR/ TM
Powertrain
Engine 4.9 L Tipo F113 and Tipo 113 B flat-12
Transmission 5-speed manual
Manufacturer Ferrari
Production 1984–1996
Assembly Maranello, Italy
Designer Leonardo Fioravanti, Ian Cameron, Guido Campoli, Emanuele Nicosia, Diego Ottina at Pininfarina[1]
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Body style 2-door berlinetta
Layout Rear mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive
TESTAROSSA
Powertrain
Engine 4.9 L Tipo F113 F12[3][9]
Power output 287 kW (390 PS; 385 hp)
Transmission 5-speed manuaL
Production 1985–1991 (7,177 produced)[3]
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,550 mm (100.4 in)[3]
Length 4,485 mm (176.6 in)[3]
Width 1,976 mm (77.8 in)[3]
Height 1,130 mm (44.5 in)[3]
Curb weight 1,708.2 kg (3,766 lb)
512 TR
Powertrain
Engine 4.9 L Tipo F113 D F12[23][24]
Power output 319 kW (434 PS; 428 hp)
Production 1992–1994 (2,261 produced)
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,550 mm (100.4 in)
Length 4,480 mm (176.4 in)
Width 1,976 mm (77.8 in)
Height 1,135 mm (44.7 in)
Curb weight 1,656 kg (3,650 lb)

F 512 M
Production 1995–1996 (501 produced)[2][30]
Powertrain
Engine 4.9 L Tipo F113 G Flat-12[31][32]
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,550 mm (100.4 in)[31]
Length 4,480 mm (176.4 in)[31]
Width 1,976 mm (77.8 in)[31]
Height 1,135 mm (44.7 in)[31]
Curb weight 1,631 kg (3,596 lb)[33] height
550
Engine 5.5 L Tipo F133A/C V12
Transmission 6-speed manual
Production 1996–2002
3,083 (550)
448 (Barchetta)
Assembly Maranello, Italy
Designer Lorenzo Ramaciotti at Pininfarina[1]
Body and chassis
Class Grand tourer (S)
Body style 2-door berlinetta (Maranello)
2-door roadster (Barchetta)
Layout Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Related Ferrari 456
Powertrain
Wheelbase 2,500 mm (98.4 in)
Length 4,550 mm (179.1 in)
Width 1,935 mm (76.2 in)
Height 1,277 mm (50.3 in) (berlinetta)
1,258 mm (49.5 in) (barchetta)
Kerb weight 1,774 kg (3,912 lb)
BARCHETTA PINNIFERIA

575M MARNELLO
Engine 5.7 L Tipo F133E/G V12
Transmission 6-speed manual
6-speed ‘F1’ electrohydraulic manualProduction 2002–2006
2,056 (575M)
Body and chassis
Class Grand tourer (S)
Body style 2-door berlinetta
2-door retractable hard-top convertible (Superamerica)
Layout Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,500 mm (98.4 in)
Length 4,550 mm (179.1 in)
Width 1,935 mm (76.2 in)
Height 1,277 mm (50.3 in) Curb weight 1,853 kg (4,085 lb)[1] 1,905 kg (4,200 lb) (Superamerica)
HGTE
GTO
Engine 6.0 L (5,999 cc) Tipo F140 C/CE V12
Power output 620 PS (456 kW; 612 hp)
608 N⋅m (448 lb⋅ft) of torque
Transmission 6-speed manual
6-speed ‘F1’ electrohydraulic manual
Production 2006–2012 Model years 2007–2012
Assembly Maranello, Italy
Designer Pininfarina under Ken Okuyama[1]
Body and chassis
Class Grand tourer Body style 2-door berlinetta
2-door roadster
Layout Front mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Related Ferrari 612 Scaglietti
Wheelbase 2,750 mm (108.3 in)
Length 4,665 mm (183.7 in)
Width 1,962 mm (77.2 in)
Height 1,336 mm (52.6 in)
Kerb weight 1,793 kg (3,953 lb) GTB[2]
1,779 kg (3,922 lb) HGTE [3]
1,746 kg (3,850 lb) GTO [4]

SA APERTA
SPECS IDENTICAL TO 599
493 kW (670 PS; 661 hp) at 8,250 rpm
620 N⋅m (457 lb⋅ft) at 6,500 rpm
3.6 sec
325 km/h (202 mph)
F12BERNILETTA
Powertrain
Engine 6.3 L F140 FC V12[1]
Transmission 7-speed dual-clutch (F1 DCT)
Production 2012–2017
Assembly Maranello, Italy
Designer Ferrari Styling Centre under Flavio Manzoni, in collaboration with Pininfarina[1]
Body and chassis
Class Grand tourer (S)
Body style 2-door berlinetta
Layout Front mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Related Ferrari FF
[2]
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,720 mm (107 in)
Length 4,618 mm (181.8 in)[3]
Width 1,942 mm (76.5 in)[3]
Height 1,273 mm (50.1 in)[3]
Kerb weight 1,791 kg (3,948 lb) spanq
F12TDF
ENGINE- 6.3 litre V12 engine
YEAR 2015

812 SUPER FAST
Powertrain
Engine 6.5 L F140 GA V12
Power output 800 PS (588 kW; 789 hp)
Transmission 7-speed dual-clutch
Production April 2017 – present
Assembly Maranello, Italy
Designer Ferrari Styling Centre under Flavio Manzoni[1]
Body and chassis
Class Grand tourer (S)
Body style 2-door berlinetta
Layout Front mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Related Ferrari Monza SP
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,720 mm (107 in)
Length 4,657 mm (183.3 in)[4]
Width 1,971 mm (77.6 in)[4]
Height 1,276 mm (50.2 in)[4]
Kerb weight 1,744 kg (3,845 lb) EndFr
F430
Powertrain
Engine 4.3 L Ferrari F136 E V8
Transmission 6-speed manual
6-speed ‘F1’ electrohydraulic manual
Production 2004–2009
Model years 2005–2009
Assembly Maranello, Italy
Designer Frank Stephenson in collaboration with Pininfarina[1][2]
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Body style 2-door berlinetta
2-door spider
Layout Longitudinal, Rear mid-engine, rear-wheel drive
Dimensions
Wheelbase 102.4 in (2,601 mm)
Length 177.6 in (4,511 mm)
Width 75.7 in (1,923 mm)
Height Coupe: 47.8 in (1,214 mm)
Spider: 48.6 in (1,234 mm)
Curb weight 1,517 kg (3,344 lb)[3]
1,569 kg (3,460 lb) (Spider)[4]
1,497 kg (3,300 lb) (Scuderia Spider 16M)[5]
1,429 kg (3,150 lb) (Scuderia)
F458
Powertrain
Engine 4.5 L Ferrari F136 F V8
Transmission 7-speed dual-clutch
Production 2009–2015
Model years 2010–2015
Assembly Maranello, Italy
Designer Donato Coco in collaboration with Pininfarina[1][2]
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Body style 2-door berlinetta
2-door retractable hard-top convertible
Layout Longitudinal, rear mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,650 mm (104.3 in)[3]
Length 4,527 mm (178.2 in)[3]
Width 1,937 mm (76.3 in)[3]
Height 1,213 mm (47.8 in)[3]
Curb weight 1,565 kg (3,450 lb).

F8 tributo
Powertrain
Engine 3.9 L twin-turbocharged Ferrari F154CD V8
Transmission 7-speed dual clutch
Production 2019 (expected)
Model years 2020
Assembly Maranello, Italy
Designer Ferrari Styling Centre
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Body style 2-door berlinetta
Layout Longitudinal rear mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Related Ferrari SF90 Stradale
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,650 mm (104.3 in)[1]
Length 4,611 mm (181.5 in)[2]
Width 1,979 mm (77.9 in)[2]
Height 1,206 mm (47.5 in)[2]
Kerb weight 1,435 kg (3,164 lb)
F mondail
Manufacturer Ferrari
Production Mondial 8:1980–1982
703 produced
Mondial qv:1983–1985
1,145 (coupe) produced
629 (cabriolet) produced
Mondial 3.2:1986–1988
987 (coupe) produced
810 (cabriolet) produced
Mondial t:1988–1993
858 (coupe) produced
1,017 (cabriolet) produced
Assembly Modena, Italy
Designer Leonardo Fioravanti at Pininfarina
Body and chassis
Class Sports car
Body style 2+2 coupe
2+2 cabriolet
Mondail 8
Production 1980–1982
Body and chassis
Body style 2+2 coupe
Layout Transverse, mid-engine, rear-wheel drive
Powertrain
Engine 3.0 L Tipo F106B FI V8
Transmission 5-speed manual
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,650 mm (104.3 in)
Length 4,580 mm (180.3 in)
Width 1,790 mm (70.5 in)
Height 1,250 mm (49.2 in)
Curb weight 1,569 kg (3,459 lb)

Mondail quatravalvolle
Production 1982–1985
Body and chassis
Body style 2+2 coupe
2+2 cabriolet
Layout Transverse, mid-engine, rear-wheel drive
Powertrain
Engine 3.0 L Tipo F105A 32V V8
Transmission 5-speed manual
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,650 mm (104.3 in)
Length 4,580 mm (180.3 in)
Width 1,790 mm (70.5 in)
Height 1,260 mm (49.6 in)
Curb weight 1,555 kg (3,428 lb)
1,607 kg (3,543 lb) (Cabriolet)
Mondail 3.2
Production 1985–1988
Body and chassis
Body style 2+2 coupe
2+2 cabriolet
Layout Transverse, mid-engine, rear-wheel drive
Powertrain
Engine 3.2 L Tipo F105C 4v V8
Transmission 5-speed manual
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,650 mm (104.3 in)
Length 4,535 mm (178.5 in)
Width 1,795 mm (70.7 in)
Height 1,235 mm (48.6 in)
1,265 mm (49.8 in) (Cabriolet)
Curb weight 1,540 kg (3,395 lb)
1,607 kg (3,543 lb) (Cabriolet) MsoNorm
Mondail t
Production 1988–1993 (MY 1989-1993) Coupe: 858 (45 RHD)
43 Imported to USA/Canada
Cabriolet: 1,017 (51 RHD)
379 Imported to USA
Body and chassis
Body style 2+2 coupe
2+2 cabriolet
Layout Longitudinal, mid-engine, rear-wheel drive
Powertrain
Engine 3.4 L Tipo F119D/G V8
Transmission 5-speed manual
Valeo auto-manual
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,650 mm (104.3 in)
Length 4,535 mm (178.5 in)
Width 1,810 mm (71.3 in)
Height 1,235 mm (48.6 in)
Curb weight 1,560 kg (3,439 lb)
1,570 kg (3,461 lb) (Cabriolet)
F365 gta 2+2
Engine-
365 GT4 2+2
F 101 AC 000
4.4 L (4,390.35 cc)
81 x 71 mm
Carburetor
340 PS (250 kW; 340 bhp) at 6200[4
Production 1972–1989
2907 produced in total
Designer Leonardo Fioravanti at Pininfarina
Body and chassis
Class Grand tourer
Layout Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Related Ferrari 365 GTC/4[1]
Chronology
Predecessor Ferrari 365 GT 2+2
Successor Ferrari 456
400 gt automatic
Overview
Production 1976–1979
355 (A), 147 (GT) produced
Powertrain
Engine 4.8 L F 101 C V12[6]
Transmission 5-speed manual
3-speed automatic
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,700 mm (106.3 in)
Length 4,810 mm (189 in)
Width 1,796 mm (70.7 in)
Height 1,310 mm (51.6 in)
Curb weight 1,700 kg (3,748 lb)
400gtI
Overview
Production 1979–1985
422 (GT) & 883 (A) produced
Powertrain
Engine 4.8 L F 101 D V12
Transmission 5-speed manual
3-speed automatic
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,700 mm (106.3 in)
Length 4,810 mm (189 in)
Width 1,798 mm (70.8 in)
Height 1,314 mm (51.7 in)
Curb weight 1,830 kg (4,034 lb)

F412
Production 1985–1989
270 (GT) and 306 (A) produced
Powertrain
Engine 4942 cc F 101 EL V12
Transmission 5-speed manual
3-speed automatic
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,700 mm (106.3 in)
Length 4,810 mm (189 in)
Width 1,798 mm (70.8 in)
Height 1,314 mm (51.7 in)
Curb weight 1,805–1,810 kg (3,979–3,990 lb)
F 456
Powertrain
Engine 5.5 L Tipo F116B/C V12 (456)
5.5 L Tipo F116C V12 (456M)
Power output 442 PS (325 kW; 436 hp)
Transmission 6-speed manual
4-speed automatic
Production 1992–1997 (456)
1998–2003 (456M)
3,289 produced[1][better source needed]
Designer Pietro Camardella[2] under Lorenzo Ramaciotti at Pininfarina[3]
Body and chassis
Class Grand tourer (S)
Body style 2-door 2+2 coupé
Layout Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Related Ferrari 550
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,600 mm (102.4 in)
Length 4,730 mm (186.2 in)
4,763 mm (187.5 in) (456M)
Width 1,920 mm (75.6 in)
Height 1,300 mm (51.2 in)
Kerb weight 1,690–1,770 kg (3,726–3,902 lb) (dry).
Production 2008[2]–2013
Model years 2009–2014
Designer Pininfarina under Ken Okuyama
Powertrain
Engine 4.3 L Ferrari F136 I V8
Transmission 7-speed dual-clutch
6-speed manual
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,670 mm (105.1 in)[1]
Length 4,563 mm (179.6 in)[1]
Width 1,902 mm (74.9 in)[1]
Height 1,308 mm (51.5 in)[1]
Kerb weight
1,735 kg (3,825 lb) (Europe)
1,870 kg (4,123 lb) (US)

F califonia T
Production 2014–2017
Model years 2015–2018
Designer Ferrari Styling Centre in collaboration with Pininfarina[23]
Powertrain
Engine 3.9 L Ferrari F154 BB twin-turbo V8
Transmission 7-speed dual-clutch[24]
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,670 mm (105.1 in)
Length 4,570 mm (179.9 in)
Width 1,910 mm (75.2 in)
Height 1,322 mm (52.0 in)
Kerb weight
1,730 kg (3,813 lb) (Europe)
1,843 kg (4,064 lb) (US)
612 scaglietti
production 2004–2011
3,025 produced
Designer Ken Okuyama at Pininfarina
Body and chassis
Class Grand tourer (S)
Body style 2-door 2+2 coupé
Layout Front mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Powertrain
Engine 5.7 L Tipo F133F/H V12
Transmission 6-speed manual
6-speed F1A electrohydraulic manual
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,950 mm (116.1 in)
Length 4,902 mm (193.0 in)
Width 1,957 mm (77.0 in)
Height 1,344 mm (52.9 in)
Kerb weight 1,850 kg (4,078.6 lb)-1,865 kg (4,111.6 lb)
FF
Production 2011–2016
2,291 produced
Assembly Maranello, Italy
Designer Pininfarina [1] and Ferrari Styling Centre under Flavio Manzoni
Body and chassis
Class Grand tourer (S)
Body style 3-door shooting-brake
Layout Front mid-engine, four-wheel-drive[2]
Powertrain
Engine 6.3 L F140 EB V12
Transmission 7-speed dual-clutch
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,990 mm (117.7 in)[3]
Length 4,907 mm (193.2 in)[3][4]
Width 1,953 mm (76.9 in)[3][4]
Height 1,379 mm (54.3 in)[3][4]
Kerb weight 1,880 kg (4,145 lb)

GTC4 lusso
Production 2016–present
Assembly Maranello, Italy
Designer Ferrari Styling Centre under Flavio Manzoni[1]
Body and chassis
Class Grand tourer (S)
Body style 3-door shooting-brake
Layout Front mid-engine, all-wheel drive / rear-wheel drive (GTC4Lusso T)
Powertrain
Engine
3.9 L twin-turbocharged Ferrari F154 BD V8 (GTC4Lusso T)
6.3 L Ferrari F140 ED V12 (GTC4Lusso)
Transmission 7-speed dual-clutch
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,990 mm (117.7 in)
Length 4,922 mm (193.8 in)[2]
Width 1,980 mm (78.0 in)[2]
Height 1,383 mm (54.4 in)[2]
F PORTOFINO
Production 2018–present
Assembly Maranello, Italy
Designer Ferrari Styling Centre under Flavio Manzoni
Body and chassis
Class Grand tourer (S)
Body style 2-door, 2+2 retractable hardtop convertible
Layout Front mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Powertrain
Engine 3.9 L Ferrari F154BD V8 (twin-turbocharged)
Transmission 7-speed dual-clutch
Dimensions
Length 4,586 mm (180.6 in)
Width 1,938 mm (76.3 in)
Height 1,318 mm (51.9 in)
Kerb weight 1,664 kg (3,668 lb) (with fluids)
250gto
Production 1962–1964
(36 produced)
Designer Giotto Bizzarrini
Sergio Scaglietti
Body and chassis
Class Sports car
Body style 2-door berlinetta
Layout FR layout
Related 330 LMB
250 LM
Powertrain
Engine 2,953 cc (3.0 L; 180.2 cu in)
Tipo 168 Comp/62 60º V12
SOHC 2 valves per cylinder valvetrain configuration
6 Weber 38 DCN carburetors
300 PS (296 hp; 221 kW) @ 7500 rpm
294 N⋅m; 217 lbf⋅ft (30 kg⋅m) @ 5500 rpm
Compression ratio 9.7:1 [1][2][3]
Transmission 5-speed Dog-leg manual
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,400 mm (94.5 in)
Length 4,325 mm (170.3 in)
Width 1,600 mm (63.0 in)
Height 1,210 mm (47.6 in)
Curb weight 880 kg (1,940 lb)

288gto
Also called Ferrari GTO
Production 1984–1987
272 produced[1]
Designer Leonardo Fioravanti at Pininfarina
Body and chassis
Class Sports car
Body style 2-door berlinetta
Layout Rear mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Related Ferrari 308 GTB/GTS
Powertrain
Engine 2.9 L (2,855 cc) F114 B 000 twin turbo V8[2]
Power output 400 PS (294 kW; 395 bhp) and 496 N⋅m (366 lbf⋅ft) of torque
Transmission 5-speed manual[2]
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,450 mm (96.5 in)[2]
Length 4,290 mm (168.9 in)[2]
Width 1,910 mm (75.2 in)[2]
Height 1,120 mm (44.1 in)[2]
Kerb weight 1,160 kg (2,557.4lb)
F40
Production 1987–1992
1,311 produced[1][2][3]
Assembly Maranello, Italy
Designer Leonardo Fioravanti and Pietro Camardella[4] at Pininfarina[2]
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Body style 2-door berlinetta
Layout Longitudinally-mounted, rear mid-engine, rear-wheel drive[5]
Powertrain
Engine 2,936 cc (2.9 L) twin-turbocharged Tipo F120A/F120D 90° V8[1][6]
Power output 478 PS (352 kW; 471 hp)[1]
484 PS; 356 kW (477 hp) US-spec[6]
Transmission 5-speed manual
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,450 mm (96 in)
Length 4,358 mm (171.6 in)
Width 1,970 mm (78 in)
Height 1,124 mm (44.3 in)
Curb weight 1,254–1,369 kg (2,765–3,018 lb)
F50
Production 1995–1997[1]
349 produced
Assembly Maranello, Italy
Designer Lorenzo Ramaciotti[2] and Pietro Camardella[3] at Pininfarina
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Body style 2-door Targa top
Layout Rear mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Related Ferrari F50 GT
Ferrari Mythos
Ferrari 333 SP
Powertrain
Engine 4.7 L DOHC 65 degree Tipo F130B V12[4] [5]
Power output 382 kW (519 PS; 512 hp)
Transmission 6-speed manual
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,580 mm (101.6 in)
Length 4,480 mm (176.4 in)
Width 1,986 mm (78.2 in)
Height 1,120 mm (44.1 in)
Curb weight 3,080 lb (1,397 kg)

F50 gt
Also called Ferrari F50 GT1
Production 1996
3 produced
Model years 1996
Assembly Maranello, Italy
Designer Pininfarina
Body and chassis
Class Race car
Body style 2-door Coupé
Layout Rear mid-engine, rear-wheel drive
Related Ferrari F50
Powertrain
Engine 4.7 L (4,698.50 cc) Tipo F130B V12 [1]
Power output 750 PS (552 kW; 740 hp)
Transmission 6-speed sequential
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,580 mm (101.6 in)
Length 4,578 mm (180.2 in)
Width 1,986 mm (78.2 in)
Height 1,092 mm (43.0 in)[2]
Curb weight 909.4 kg (2,005 lb)
860 kg (1,896 lb) dry
Enzo
Production 2002–2004[1][2]
400 produced[3]
Assembly Maranello, Italy
Designer Ken Okuyama at Pininfarina
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Body style 2-door berlinetta
Layout Rear mid-engine, rear-wheel drive
Doors Butterfly
Related
Ferrari FXX
Maserati MC12
Ferrari P4/5
Maserati Birdcage 75th
Powertrain
Engine 6.0 L Tipo F140 B V12
Power output 660 PS (485 kW; 651 hp)
Transmission 6-speed ‘F1’ electrohydraulic manual
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,650 mm (104 in)
Length 4,702 mm (185.1 in)
Width 2,035 mm (80.1 in)
Height 1,147 mm (45.2 in)
Curb weight 1,480 kg (3,260 lb)
La Ferrari
Production
June 2013 – January 2016 (coupé, 500+ examples)
October 2016 – August 2018 (Aperta, 210 examples)
Model years 2013–2016 (coupé)
2016–2018 (Aperta)
Designer Centro Stile Ferrari under Flavio Manzoni[1]
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Body style 2-door coupé
2-door roadster (Aperta)
Layout Rear mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Doors Butterfly doors (coupé)
Swan doors (Aperta)
Related Ferrari FXX-K
Powertrain
Engine 6.3 L F140FE V12
Electric motor 1 electric motor and KERS
Power output 708 kW (963 PS; 949 hp)
Transmission 7-speed dual-clutch automated manual
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,650 mm (104.3 in)
Length 4,702 mm (185.1 in)
Width 1,992 mm (78.4 in)
Height 1,116 mm (43.9 in)
Kerb weight 1,585 kg (3,495 lb)

Fxx
Production 2005–2007 (38 produced)
Assembly Maranello, Italy
Designer Frank Stephenson[1]
Body and chassis
Class Track day car
Development prototype
Body style 2-door berlinetta
Layout Rear mid-engine, rear-wheel drive
Doors Butterfly
Related Enzo Ferrari
Maserati MC12 Corsa
Powertrain
Engine 6.3 L (6,262.45 cc) F140 V12[2]
Transmission 6-speed ‘F1’ electrohydraulic manual
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,650 mm (104.3 in)
Length 4,832 mm (190.2 in)
Width 2,040 mm (80.3 in)
Height 1,127 mm (44.4 in)
Curb weight 1,155 kg (2,546 lb) (Dry weight)
Testing
Engine: 6,262.5 cc (6.26245 L)[2] longitudinal, rear-mid-mounted, 65-degree, naturally aspirated aluminium V12
Valvetrain: DOHC, 4 valves per cylinder with continuously variable timing
Fuel system: Bosch Motronic ME7 Sequential Electronic Injection
Max power: 588 kW (799 PS; 789 hp) at 8,500 rpm[2]
Max torque: 686 N⋅m (506 lb⋅ft) at 5,750 rpm[2]
Specific Output: 93 kW (126 PS; 125 hp) per litre[2]
Drivetrain: Rear-wheel drive with Traction control system
Construction: Carbon fibre body over carbon fibre tub with rear alloy subframe
Front brakes: Brembo CCM (carbon-ceramic) discs with 6-piston calipers, power assist ABS
Rear brakes: Brembo CCM (carbon-ceramic) discs with 4-piston calipers, power assist ABS
0–97 km/h (0–60 mph) acceleration: 2.77 seconds
Front wheels (dimensions): 483 mm (19.0 in) x 229 mm (9.0 in)
Rear wheels (dimensions): 483 mm (19.0 in) x 330 mm (13.0 in)
Steering: Rack and pinion with power assistance
Suspension: Double wishbones with push-rod actuated coil-shock units, adaptive dampers, electronic shock absorbers, anti-roll bar
Front track: 1,660 mm (65.4 in)
Rear track: 1,650 mm (65.0 in)
Rear view is provided by a roof mounted video camera displayed on a small inboard screen.
Top Speed: 345 km/h (214 mph)
Fxx-k
Production 2015–2017
(40 built)
Assembly Maranello, Italy
Designer
Flavio Manzoni
Marco Fainello
Evan Rodriguez
Body and chassis
Class Track day car
Developmental prototype
Body style 2-door berlinetta
Layout Rear mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Doors Butterfly
Related LaFerrari
Powertrain
Engine 6.3 L naturally aspirated F140 V12
Electric motor 140 kW (190 PS; 188 hp) KERS style electric motor
Power output 632 kW (859 PS; 848 hp)(engine)
1,050 PS (1,036 hp; 772 kW) (total output)
Transmission 7-speed dual-clutch
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,650 mm (104 in)
Length 4,896 mm (192.8 in)
Width 2,051 mm (80.7 in)
Height 1,116 mm (43.9 in)
Curb weight 1,495 kg (3,296 lb) with fluids
1,165 kg (2,568 lb) dry
Fxx-k evo
Body and chassis
Body style 2-door berlinetta
Layout Rear mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Powertrain
Engine 6.3 L naturally aspirated F140 V12
Transmission 7-speed dual-clutch
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,650 mm (104 in)
Length 4,896 mm (192.8 in)
Width 2,051 mm (80.7 in)
Height 1,116 mm (43.9 in)
Curb weight 1,405 kg (3,097 lb) with fluids
1,075 kg (2,370 lb) dry

125 f1
Manufacturer Ferrari
Production 1948–1950
Designer Gioacchino Colombo, Valerio Colotti
Body and chassis
Class Formula One car
Powertrain
Engine 1.5 L Colombo 125 V12
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2160 mm (85 in)
2320 mm (91 in)
Length 3685 mm (145 in)
Width 1400 mm (55 in)
Height 1025 mm (40 in)
Curb weight 710 kg (1565 lb)
Ferrari 375
1951 Ferrari 375F1.jpg
Ferrari 375 F1
Category Formula One
Constructor Ferrari
Designer(s) Aurelio Lampredi
Predecessor 125
Successor 500
Technical specifications[1][2][3]
Chassis Single-seater, tubular frame
Wheelbase 2,320 mm (91 in)
2,420 mm (95 in)
Engine 3.3 L Lampredi V12, naturally aspirated, front engine, longitudinally mounted
4.1 L Lampredi V12, naturally aspirated, front engine, longitudinally mounted
4.5 L Lampredi V12, naturally aspirated, front engine, longitudinally mounted
Transmission Ferrari 4-speed manual
Weight 560 kg (1,230 lb)
Fuel Shell
Tyres Pirelli
Firestone
Sf90
Formula One Test Days 2019 – Ferrari SF90 – Sebastian Vettel.jpeg
Sebastian Vettel driving the SF90 during pre-season testing
Category Formula One
Constructor Ferrari
Designer(s)
Mattia Binotto (Technical Director)
Predecessor Ferrari SF71H
Technical specifications
Suspension (front) Push-rod
Suspension (rear) Pull-rod
Length 5,712 mm (224.9 in)
Width 2,000 mm (79 in)
Height 950 mm (37 in)
Wheelbase 3,652 mm (143.8 in)
Engine Ferrari 064 1.6 L (98 cu in) direct injection V6 turbocharged engine limited to 15,000 RPM in a mid-mounted, rear-wheel drive layout
Electric motor Ferrari kinetic and thermal energy recovery systems
Transmission Eight forward and one reverse gears
Power 1000-1050 hp
Weight 743 kg (1,638 lb)
Fuel Shell V-Power
Lubricants Shell Helix Ultra
Brakes Self-ventilating Brembo Carbon disc brakes (front and rear) with electronic control on rear brakes
Tyres Pirelli P Zero (dry)
Pirelli Cinturato (wet)
OZ forged magnesium wheels: 13
ROLLS ROYCE

Rolls Royce 10hp
Year-1904-1906
Engine1800cc/1995cc
Transmission-3speed
Rolls royce 15hp
Engine- 3000cc 3cyl
Transmission-3speed
Rolls Royce (silver ghost)
Engine- straight 6
7036cc (429.4cid) (1906–1910)
7428cc (453.3cid) (from 1910)
Transmission- 3-speed manual (1909–1913)
4-speed manual (from 1913)
Rolls Royce v8
Year-1905
Engine- 3535 cc V-8 bore x stroke: 82.5 by 82.5 millimetres (3.25 in × 3.25 in)
Transmission three-speed
Rolls-royce 30hp
Year-1904
Engine-6000cc/ 6cylinder
Transmission- 4 speed
RR TWENTY
Engine 3,127 cc (3.1 L) I6
Transmission 3-speed manual 4-speed manual
Production 1922-1929
2940 made
Designer Sir Henry Royce
Body and chassis
Body style 4-door convertible
4-door sedan
Layout FR layout

RR NEW PHANTOM
Engine 7,668 cc (468 cu in) I6
Transmission 3-speed manual 4-speed manual
Also called 40/50 Phantom
Production 1925–1931
3512 produced
Assembly Derby, England Springfield, Massachusetts
Body and chassis
Class Luxury car
Body style 4-door saloon
Layout FR layout
RR TWENTY TWENTY FIVE
Engine 3669 cc Transmission 4-speed manual
Production 1929-1936
3827 made
Body and chassis
Body style dependant on coachbuilder
RR PHANTOM II
Powertrain
Engine 7668 cc I6
Transmission 4-speed manual
Production 1929–1936
1680 produced
Body and chassis
Class Luxury car

RR 25/30
Powertrain Engine 4257 cc Transmission 4-speed manual
Manufacturer Rolls-Royce Ltd Production 1936–1938 1201 made
RR PHANTOM III
Powertrain
Engine 7338 cc (447 cubic inches) V12
Transmission 4-speed manual
Production 1936–1939
727 produced
Body and chassis, Class Luxury car
RR WRAITH
Powertrain
Engine 4257 cc Straight 6 Transmission 4 speed manual
Production 1938–39 (chassis)
491 cars/492 chassis built
Body and chassis
Related Bentley Mark V

RR SILVER WRAITH
Related Rolls-Royce Silver Dawn
Powertrain
Engine 4.3 L (260 cu in) I6 (1946–51) 4.6 L (280 cu in) I6 (1951–55) 4.9 L (300 cu in) I6 (1955–58)
Transmission 4-speed manual with synchromesh
4-speed Hydramatic automatic optional from 1952
Production 1946–1958
1883 produced (incl. 639 LWB cars)
Body and chassis
Class Full-size luxury car (F)
Body style 4-door saloon
Layout Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive
RR SILVER DAWN
Powertrain
Engine 4.2 L (260 cu in) I6
4.6 L (280 cu in) I6
Transmission 4-speed manual or 4-speed automatic
Production 1949–1955
760 made[1]
Body and chassis Class Full-size luxury car (F)
Body style 4-door saloon Layout Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive
RR PHANTOM IV
Engine 5.7 L and 6.5 L (final three vehicles only) I8
Transmission 4-speed gearbox (from 1954, 4-speed automatic gearbox standard)
Production 1950–1956
18 vehicles Assembly United Kingdom

RR SILVER CLOUD
Powertrain
Engine 4.9 L (300 cu in) I6
6.2 L (380 cu in) V8 Transmission 4-speed automatic
Production 1955–1966 7,372 produced Assembly Crewe, England
Dimensions Kerb weight 4,647 lb (2,108 kg)
PHANTOM V
Powertrain Engine 6,230 cc Rolls-Royce V8 Transmission 4-speed automatic
Production 1959–1968 832 produced
Assembly Crewe, England
(engine and chassis) Designer Park Ward for model #980 or James Young for model #2003
Body and chassis Body style 4-door sedan Layout FR layout
ROLLS ROYCE SILVER SHADOW
Powertrain
Engine
6230 cc L410 V8 (1965–70) 6750 cc L410 V8 (1970–80)
Transmission 4-speed Hydramatic automatic (1965–70; UK only)
3-speed THM 400 automatic
Production 1965–1980
30,057 produced
Assembly Crewe, England
Body and chassis
Body style
2-door coupé
2-door cabriolet
4-door saloon
Layout Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Related Bentley T-series
Rolls-Royce Camargue
Rolls-Royce Corniche

SILVER SHADOW II
1977
several major changes
notably rack and pinion steering
the bumpers
to alloy and rubber
more ground clearance
PHANTOM VI
Powertrain
Engine
6.2-litre (380 cubic inch) Rolls-Royce V8 (1968–1978) 6.75-litre (412 cubic inch) Rolls-Royce V8 (1979–1990
Production 1968–1990
374 produced (mostly before 1979)
Assembly West Sussex, England
Body and chassis
RR CORNICHE
Powertrain Engine 6.75 L L410 OHV V8
Production 1966–1995
Designer Bill Allen
Body and chassis
Body style 2-door coupé
2-door convertible
Layout FR layout

RR CAMERGUE
Powertrain
Engine 6.75 L (412 cid) Rolls-Royce V8
Transmission 3-sp TH400 automatic
Production 1975–1986
531 produced
Designer Paolo Martin for Pininfarina[1][2][3]
Body and chassis
Class Luxury car
Body style 2-door saloon
Layout FR layout
Related Rolls-Royce Silver Shadow
Rolls-Royce Corniche
Bentley T-series
RR SILVER SPIRIT MARK1
its 6.75 L L410 V8 engine
3-speed automatic gearbox
with Girling automatic
hydraulic ride height
gas-charged shock absorbers
RR SILVER SPIRIT MARK 2
Production 1989–1993
Powertrain
Engine 6.75 L Rolls-Royce L410 V8
Transmission 3-speed GM THM400 automatic (1989-Winter 1991) 4-speed GM 4L80E automatic (Winter 1991-)

MARK 3
Production 1993–1996
Powertrain Engine 6.75 L Rolls-Royce L410 V8 Transmission 4-speed GM
MARK 4
Production 1995–1999
Powertrain
Engine 6.75 L Rolls-Royce L410 V8
Transmission 4-speed automatic
SILVER SERAPH
Powertrain
Engine 5.4 L BMW M73 V12
Transmission 5-speed ZF 5HP30 automatic
Production 1998–2002
Assembly United Kingdom: Crewe, England
Designer Steve Harper under Graham Hull
Body and chassis
Class Full-size luxury car (F)
Body style 4-door saloon
Layout Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Related Bentley Arnage

RR PHANTOM 7
Powertrain
Engine 6.75 L N73B68 V12 (petrol)
Transmission
6-speed 6HP32 automatic (Series I models)
8-speed 8HP70 automatic (Series II models)
Production 2003–2017 (saloon) 2007–2016 (Drophead Coupé) 2008–2016 (Coupé)
Body and chassis
Class Ultra-luxury car (F)
Body style 4-door saloon
2-door convertible
2-door coupé
Layout FR layout
Related Rolls-Royce Phantom Drophead Coupé
Rolls-Royce Phantom Coupé
DROPHEAD PHANTOM
Powertrain
Engine V12 6,749 cc (412 cu in)
Transmission 6-speed automatic
Production 2007-2016
Assembly Goodwood plant, Chichester, West Sussex, UK
Body and chassis
Class Luxury car (F)
Body style 2-door convertible
Layout FR layout
Doors Suicide doors
Related Rolls-Royce Phantom Coupé
RR PHANTOM COUPE
Powertrain
Engine 6.75 L V12 453 bhp (338 kW; 459 PS)
Transmission 6-speed automatiC
Production 2008–2017
Assembly United Kingdom: Chichester, West Sussex, England (Goodwood plant)
Body and chassis
Class Luxury car (F)
Body style 2-door coupé
Layout FR layout
Doors Suicide doors
Related Rolls-Royce Drophead

RR GHOST
Powertrain
Engine 6.6 L N74B66 V12-T
Transmission 8-speed 8HP90 automati
Production 2009–present
Model years 2010–present
Assembly United Kingdom: West Sussex, England (Goodwood plant)
Designer
Andreas Thurner (2006)
Charles Coldham (interior)
Body and chassis
Class Full-size luxury car (F)
Body style 4-door saloon Layout FR layout
Wraith
Powertrain
Engine 6,592 cc (402.3 cu in) BMW N74 twin-turbo V12[1]
Transmission 8-speed ZF 8HP automatic
Production 2013–present
Model years 2014–present
Assembly United Kingdom: Goodwood, England (Goodwood manufacturing)
Designer Pavle Trpinac
Body and chassis
Class Grand tourer (F)
Body style 2-door hardtop coupé
Layout FR layout
Platform BMW F01
Doors Suicide doors
Powertrain
Engine 6,592cc BMW N74 Twin-turbo V12
Transmission 8-speed ZF 8HP automatic
Manufacturer Rolls-Royce Motor Cars
Production 2015–present
Model years 2016–present
Assembly United Kingdom
Designer Giles Taylor[1]
Body and chassis
Class Grand tourer (F)
Body style 2-door convertible
Layout FR layout
Doors Suicide doors

RR CULLIAN
Powertrain
Engine 6.75 L N74B68 twin-turbocharged V12 (petrol)
Transmission 8-speed 8HP automatic
Manufacturer Rolls-Royce Motor Cars
Production 2018–present
Assembly United Kingdom: West Sussex, England (Goodwood plant)
Designer Giles Taylor[1]
Body and chassis
Class Full-size luxury SUV
Body style 5-door SUV
Layout Front-engine, four-wheel-drive layout
Platform Architecture of Luxury
ROLLS ROYCE PHANTOM VIII
Powertrain
Engine 6.75 L N74B68 twin-turbocharged V12 (petrol)
Transmission 8-speed 8HP automatic
Production 2017–present
Assembly United Kingdom: West Sussex, England (Goodwood plant)
Designer Giles Taylor[1][2][3]
Pavle Trpinac[4]
Chris Duff (interior)
Body and chassis
Class Full-size luxury car
Ultra-luxury car (F)
Body style 4-door saloon
Layout FR layout
Platform Architecture of Luxury
lamborghini

Lamborgini 350gt
Powertrain
Engine 3.5 L V12
Transmission 5-speed ZF manual
Production 1963
Designer Giorgio Prevedi, under the supervision of Franco Scaglione
Body and chassis
Class Prototype / Sports car
Body style 2-door grand tourer coupé
Layout Longitudinal front-engine, rear-wheel drive
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,450 mm (96.5 in)
Length 4,370 mm (172.0 in)
Width 1,760 mm (69.3 in)
Height 1,050 mm (41.3 in)
Kerb weight 1,292 kg (2,848 lb)
350gt redesigned
Powertrain
Engine 3,464 cc (211.4 cu in) 60° aluminium V12 DOHC
Power output 280 bhp (284 PS; 209 kW) and 325 N⋅m (240 lbf⋅ft) of torque
Transmission 5-speed ZF manual2]
Production May 1964–19662]
120 built1]
Assembly Italy: Sant’Agata2]
Designer Carrozzeria Touring
Body and chassis
Class Grand tourer
Body style 2-door coupé
Layout FR layout
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,550 mm (100.4 in)
Width 1,730 mm (68.1 in)
Height 1,220 mm (48.0 in)
Kerb weight 1,450 kg (3,197 lb)
400gt
Powertrain
Engine 3,929 cc V12
Transmission 5-speed manual
Also called Lamborghini 400 GT 2+2
Production 1966–1968
247 built1]
Designer Carrozzeria Touring
Body and chassis
Class Grand tourer
Body style 2-door coupé
Layout FR layout
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,550 mm (100.4 in)
Length 4,470 mm (176.0 in)
Width 1,727 mm (68.0 in)
Height 1,257 mm (49.5 in)
Kerb weight 1,472 kg (3,245 lb)

Miura
p400
Powertrain
Engine 3929 cc V12
Transmission 5-speed manual
Production 1966–731]
764 built
Designer Marcello Gandini at Bertone2]
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Body style 2-door coupé
Layout Transverse rear mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,500 mm (98.4 in)
Length 4,360 mm (171.7 in)
Width 1,760 mm (69.3 in)
Height 1,050 mm (41.3 in)
Curb weight 1,292 kg (2,848 lb)
Miura
p400s
Powertrain
Engine 3929 cc V12
Transmission 5-speed manual
Production 1966–731]
764 built
Designer Marcello Gandini at Bertone2]
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Body style 2-door coupé
Layout Transverse rear mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,500 mm (98.4 in)
Length 4,360 mm (171.7 in)
Width 1,760 mm (69.3 in)
Height 1,050 mm (41.3 in)
Curb weight 1,292 kg (2,848 lb)
Miura
p400sv
Powertrain
Engine 3929 cc V12
Transmission 5-speed manual
Production 1966–731]
764 built
Designer Marcello Gandini at Bertone2]
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Body style 2-door coupé
Layout Transverse rear mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,500 mm (98.4 in)
Length 4,360 mm (171.7 in)
Width 1,760 mm (69.3 in)
Height 1,050 mm (41.3 in)
Curb weight 1,292 kg (2,848 lb)

Miura
p400jota
Powertrain
Engine 3929 cc V12
Transmission 5-speed manual
Production 1966–731]
764 built
Designer Marcello Gandini at Bertone2]
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Body style 2-door coupé
Layout Transverse rear mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,500 mm (98.4 in)
Length 4,360 mm (171.7 in)
Width 1,760 mm (69.3 in)
Height 1,050 mm (41.3 in)
Curb weight 1,292 kg (2,848 lb)
Flying star ii
Also called Lamborghini 400 GT Flying Star II
Production 1966
Body and chassis
Body style 2-door shooting-brake
Layout FR layout
Powertrain
Transmission 5-speed manual
MARZAL
Production 1967 , 1 built
Designer Marcello Gandini of Bertone
Body and chassis
Class Concept car
Layout FR layout
Doors Gull-wing
Powertrain
Engine 2.0 L I6
Transmission 5-speed manual

ISLERO
Production 1968-69
Islero: 125 units
Islero S: 100 units
Total: 225 units
Designer Mario Marazzi at Carrozzeria Marazzi
Body and chassis
Class Grand tourer
Body style 2+2 Coupé
Layout FR layout
Platform tubular steel frame
riveted aluminium body panels
Powertrain
Engine 3,929 cc (239.8 cu in) 60° V12
Transmission five-speed, reverse manual all-synchromesh
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,546 mm (100.25 in)
ESPADA
Manufacturer Lamborghini
Production 1968–1978
1217 made1]
Assembly Italy: Sant’Agata Bolognese
Designer Marcello Gandini at Bertone2]
Body and chassis
Class Grand tourer
Body style 2-door coupé
Layout FR layout
Powertrain
Engine 3.9 L Lamborghini V12
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,650 mm (104.3 in)
Length 4,730 mm (186.2 in)
Width 1,860 mm (73.2 in)
Height 1,185 mm (46.7 in) Kerb weight 1,630 kg (3,594 lb)
BRAVO
Also called Studio 114
Production 1974
Designer Marcello Gandini at Bertone
Body and chassis
Class Sports car
Layout Transverse mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Powertrain
Engine 3.0 L, 90° Aluminum L240 V8 transverse, mid-mounted DOHC per bank
Transmission 5-speed + reverse all-synchromesh
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,275 mm (89.6 in)
Length 3,775 mm (148.6 in)
Width 1,900 mm (74.8 in)
Height 1,050 mm (41.3 in)
Curb weight 1,085 kg (2,392 lb)

URRACO
Production 1972-1979
791 produced
Assembly Italy: Sant’Agata Bolognese
Designer Marcello Gandini at Bertone1]
Body and chassis
Class Sports car
Body style 2+2 coupé
Layout Transverse mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Related Lamborghini Silhouette
Lamborghini Jalpa
Lamborghini Espada
Powertrain
Engine 2.0 L (122 cu in) V8 engine (P200)
2.5 L (153 cu in) V8 engine (P250 & P111)
3.0 L (183 cu in) V8 engine (P300)
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,450 mm (96.5 in)
Length 4,250 mm (167.3 in)
Width 1,760 mm (69.3 in)
Height 1,160 mm (45.7 in)
JARAMA
Manufacturer
Lamborghini
Production
1970
–-
1976
Jarama: 176 units
Jarama S: 152 units
Total: 328 units
Assembly Italy: Sant’Agata Bolognese
Designer
Marcello Gandini at Bertone
Body and chassis
Class
Grand tourer
Body style
2-door 2+2 coupé
Layout
FR layout
Engine 3.9 L (3,929 cc) Lamborghini V12
Transmission
5-speed manual
LP500 COUNTACH
Production 1974–1990
(1,983 produced)
Assembly Italy: Sant’Agata Bolognese
Designer Marcello Gandini at Bertone (LP500 prototype)1]
Paolo Stanzani (production version)2]
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Body style 2-door coupé
Layout Longitudinal rear mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Doors Scissor
Related Lamborghini LM002
Powertrain
Engine Lamborghini V12
LP400, LP400 S: 3,929 cc (3.9 L)
LP500 S: 4,754 cc (4.8 L)
5000 QV, 25th Anniversary: 5,167 cc (5.2 L)
Transmission 5-speed synchromesh manual3]
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,450 mm (96.46 in)4]
Length 4,140 mm (162.99 in)5]

SILHOUTTE
Also called Lamborghini Silhouette P300
Production 1976 – 1979
54 produced1]
Designer Bertone
Body and chassis
Class Sports car
Body style 2-door targa
Layout Transverse mid-engine,
rear-wheel drive
Powertrain
Engine 2,995.8 cc (182.8 cu in) V8
Power output 268.9 PS (198 kW; 265 bhp) and 275 N⋅m (203 lbf⋅ft) of torque
Transmission 5-speed manual2]
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,450 mm (96.5 in)2]
Length 4,320 mm (170.1 in)1]
JALPA
Also called Lamborghini Jalpa P350
Production 1981–1988
410 produced
Assembly Italy: Bolognese, Sant’Agata
Designer Giulio Alfieri
Carrozzeria Bertone
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Body style 2-door targa
Layout Transverse mid-engine, rear-wheel drive
Powertrain
Engine 3.5-litre Lamborghini V8
Transmission 5-speed synchromesh manual
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,451 mm (96.5 in)
Length 4,330 mm (170.5 in)
Width 1,880 mm (74.0 in)
Height 1,140 mm (44.9 in)
Kerb weight 1,510 kg (3,329 lb)
COUNTACH LP5000
bored and stroked to 5,167 cc
the carburetors were replaced with Bosch K-Jetronic fuel injection system
power output of 309 kW (420 PS; 414 hp).
; 449 hp
) at 7,000 rpm
of torque at 5,200 rpm

LP5000 QUTTROVALVOLE
Lamborghini
1988 Production Car
ForzaCountry ItalyFlag Italy
, EngineType
5.2L Naturally-Aspirated V12
, BHP
455 bhp (339 kW)
, Torque
369 lb⋅ft (500 N·m)
, EngineLayout
Mid-Engined
, Mass
3284 lbs (1490 kg)
, Balance
41% / 59% Weight Distribution
, Transmission
5-speed Transmission
, DrivetrainWheel
Rear-Wheel Drive
Walter wolf version countach
the 5.0 L
333 kW (453
PS; 447 hp) at 7,900 rpm
maximum speed of 315 or 324
km/h (196 or 201 mph)
Countach Turbo S
twin-turbo configuration
accomplished between 1980 and 1982.
The Turbo S weighed 1,515 kg (3,340 lb),
its 4.8 litre twin-turbocharged V12
maximum power output of 558 kW (759 PS; 748 hp) and 876 N⋅m (646 lb⋅ft)
top speed of
335 km/h (208 mph).

Countach qvx
short-lived Group C sports racing car
displacement of 5.7-
litre
maximum power output between 485–522 kW (659–
710 PS; 650–700 hp)
LM002
Production 1986–1993
328 produced[1][2]
Assembly Italy: Sant’Agata Bolognese
Body and chassis
Class Truck
Body style
4-door pickup
4-door sport utility truck
Layout F4 layout
Platform
tubular steel frame riveted aluminium body panels Related Lamborghini Countach
Powertrain
Engine
5.2 L (5167 cc) V12
7.2 L L804 marine V12
Transmission 5-speed manual
Wheelbase 2,950 mm (116.1 in)
Length 4,790 mm (188.6 in)
Width 2,000 mm (78.7 in)
Height 1,850 mm (72.8 in) Curb weight 2,700 kg (5,952 lb)
P140
Production 1987
3 or 4 prototypes made
Designer Marcello Gandini
Body and chassis
Class Development prototype
Body style 2-door coupé
Layout Rear mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Related Lamborghini Cala
Powertrain
Engine 4.0 L V10
Transmission 6-speed manual

DIABLO
Production 1990–2001[1]
2,884 produced
Assembly Italy: Sant’Agata Bolognese
Designer
Marcello Gandini (initial design)
Tom Gale[2] at Chrysler Styling Center (final design)[3]
Luc Donckerwolke (Diablo 6.0 VT)
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Body style 2-door coupé
2-door retractable hard-top convertible (roadster)
Layout Longitudinal, Mid-engine, rear-wheel drive / all-wheel drive
Doors Scissor
Related
Vector M12
Bugatti EB118
Bugatti 18/3 Chiron
Powertrain
Engine 5.7 L V12
6.0 L V12
Transmission 5-speed manual
DIABLO S30
Production 1990–2001[1]
2,884 produced
Assembly Italy: Sant’Agata Bolognese
Designer
Marcello Gandini (initial design)
Tom Gale[2] at Chrysler Styling Center (final design)[3]
Luc Donckerwolke (Diablo 6.0 VT)
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Body style 2-door coupé
2-door retractable hard-top convertible (roadster)
Layout Longitudinal, Mid-engine, rear-wheel drive / all-wheel drive
Doors Scissor
Related
Vector M12
Bugatti EB118
Bugatti 18/3 Chiron
Powertrain
Engine 5.7 L V12
6.0 L V12
Transmission 5-speed manual
DIABLO ROADSTER
Production 1990–2001[1]
2,884 produced
Assembly Italy: Sant’Agata Bolognese
Designer
Marcello Gandini (initial design)
Tom Gale[2] at Chrysler Styling Center (final design)[3]
Luc Donckerwolke (Diablo 6.0 VT)
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Body style 2-door coupé
2-door retractable hard-top convertible (roadster)
Layout Longitudinal, Mid-engine, rear-wheel drive / all-wheel drive
Doors Scissor
Related
Vector M12
Bugatti EB118
Bugatti 18/3 Chiron
Powertrain
Engine 5.7 L V12
6.0 L V12
Transmission 5-speed manual

DIABLO VT
Production 1990–2001[1]
2,884 produced
Assembly Italy: Sant’Agata Bolognese
Designer
Marcello Gandini (initial design)
Tom Gale[2] at Chrysler Styling Center (final design)[3]
Luc Donckerwolke (Diablo 6.0 VT)
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Body style 2-door coupé
2-door retractable hard-top convertible (roadster)
Layout Longitudinal, Mid-engine, rear-wheel drive / all-wheel drive
Doors Scissor
Related
Vector M12
Bugatti EB118
Bugatti 18/3 Chiron
Powertrain
Engine 5.7 L V12
6.0 L V12
Transmission 5-speed manual
DIABLO SV
Production 1990–2001[1]
2,884 produced
Assembly Italy: Sant’Agata Bolognese
Designer
Marcello Gandini (initial design)
Tom Gale[2] at Chrysler Styling Center (final design)[3]
Luc Donckerwolke (Diablo 6.0 VT)
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Body style 2-door coupé
2-door retractable hard-top convertible (roadster)
Layout Longitudinal, Mid-engine, rear-wheel drive / all-wheel drive
Doors Scissor
Related
Vector M12
Bugatti EB118
Bugatti 18/3 Chiron
Powertrain
Engine 5.7 L V12
6.0 L V12
Transmission 5-speed manual
ATHON
Model years 1980
Designer Marc Deschamps at Bertone
Body and chassis
Layout Transverse mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive
Related Lamborghini Silhouette
Powertrain
Engine 3.0 L (183 cu in) V8 engine
Transmission 5-speed manual
Dimensions
Wheelbase 96.6 in (2,455 mm)
Length 147.2 in (3,739 mm)
Width 74.1 in (1,882 mm)
Height 41 in (1,041 mm)

Marcopolo
Production 1982
Designer Giorgetto Giugiaro at Italdesign
Body and chassis
Class Concept car Body style MR 2+2 coupe
Doors Gullwing
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,750 mm (108.3 in)
Length 4,575 mm (180.1 in)
Width 1,870 mm (73.6 in)
Height 1,300 mm (51.2 in)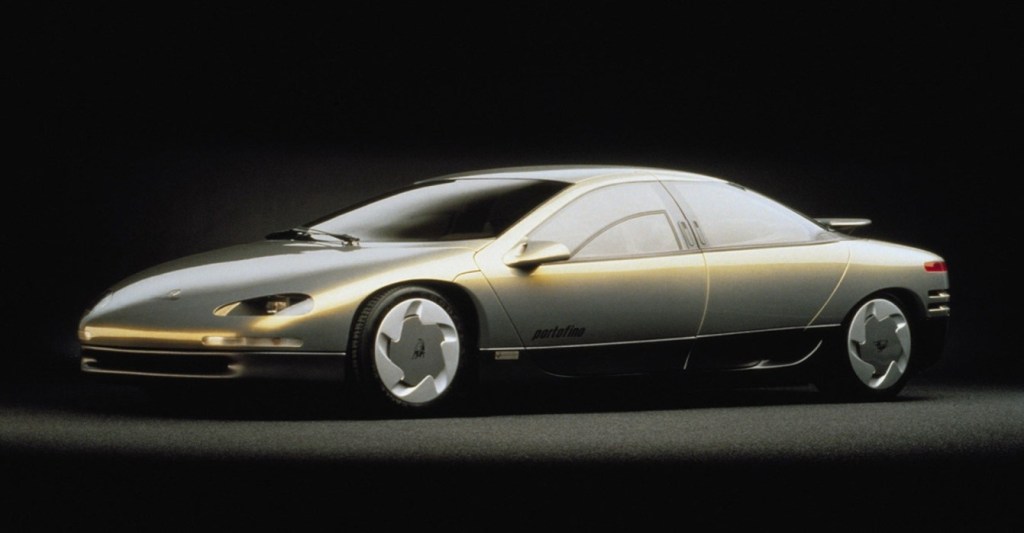
Portofino
Manufacturer Lamborghini
Also called Chrysler Portofino
Production 1 built
Model years 1987
Designer Kevin Verduyn
Body and chassis
Class Concept car
Body style 4-door sedan
Layout Mid-engine rear-wheel drive
Doors Scissor doors (front)
Suicide Scissor doors (rear)
Related Lamborghini Jalpa
Powertrain
Engine 3.5 L V8
Transmission 5-speed manual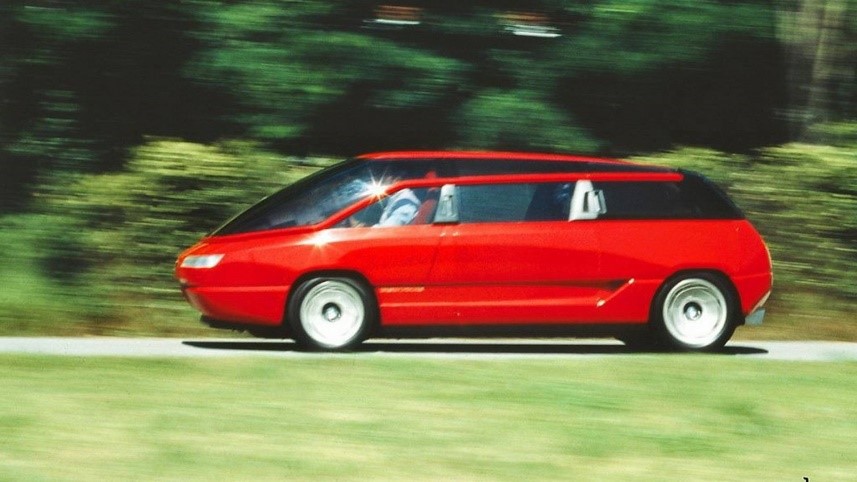
Bertone genesis
Also called Lamborghini Genesis
Production 1988
Designer Bertone
Body and chassis
Body style 5-door minivan
Layout FR layout
Doors Gullwing doors
Powertrain
Engine 5.2 L (5,167cc) V12
Transmission 3-speed TorqueFlite automatic
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,650 mm (104 in)
Length 4,475 mm (176 in)

Cala
Also called Italdesign Calà
Production 1995
1 prototype
Assembly Sant’Agata Bolognese, Italy
Designer Giorgetto Giugiaro[1]
Body and chassis
Class Concept car
Body style 2-door Targa top
Layout Rear mid-engine, rear-wheel drive
Related Lamborghini P140
Powertrain
Engine 4.0 L V10
Transmission 6-speed manual
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,522 mm (99.3 in)[1]
Length 4,390 mm (172.8 in)[1]
Width 1,900 mm (74.8 in)[1]
Height 1,222 mm (48.1 in)[1]
1,220 mm (48.0 in) (without roof)
Kerb weight 1,290 kg (2,844 lb)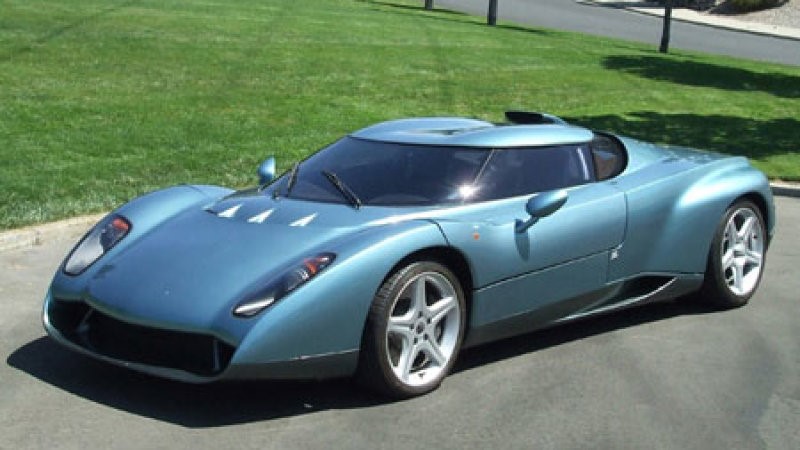
Zagato raptor
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Concept car
Body style 2-door coupé
Layout Longitudinal rear-mid-engine, all-wheel-drive
Related Lamborghini Diablo
Powertrain
Engine 5.7 L Lamborghini Diablo V12
Transmission 5-speed manual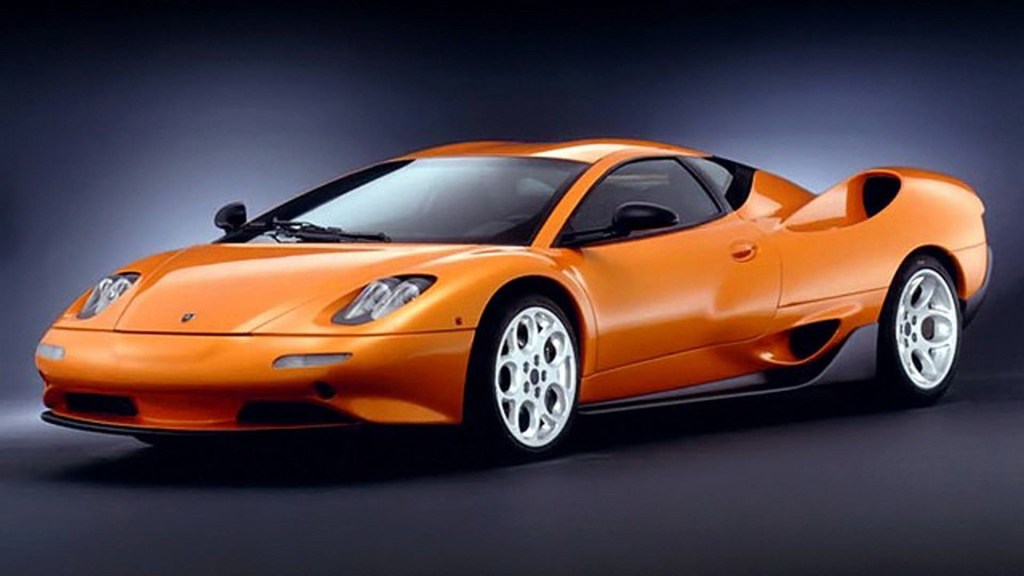
Zagato canto
Debuted: 1999
Specs: V12 6.0-liter engine with 640 horsepower, rear-wheel drive, six-speed manual gearbox, 217 mph (350 kph) top speed+

murcialago
Production 2001–2010
4,099 built[1]
Assembly Italy: Sant’Agata Bolognese
Designer Luc Donckerwolke
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Body style 2-door coupé
2-door roadster
Layout Longitudinal, Mid-engine, all wheel drive
Doors Scissor
Related Lamborghini Reventón
Powertrain
Engine 6.2 L–6.5 L V12
Power output
(580 PS) (427 kW) (2001–2005)
(640 PS) (471 kW) (2006–2010)
(650 PS) (478 kW) (LP 650-4 roadster)
(670 PS) (493 kW) (LP 670-4 SV)
Transmission 6-speed manual
6-speed e-gear semi-automatic
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,665 mm (104.9 in)
Length
2002–05: 4,580 mm (180.3 in)
2006–10: 4,610 mm (181.5 in)
Width
2002–05: 2,045 mm (80.5 in)
2006–10: 2,057 mm (81.0 in)
Height 1,135 mm (44.7 in)
Curb weight
1,841 kg (4,058 lb)[2]
1,860 kg (4,100 lb) Roadster[3]
1,746 kg (3,850 lb) LP640[4]
1,860 kg (4,100 lb) LP640 Roadster[5]
1,746 kg (3,850 lb) LP670-4 SV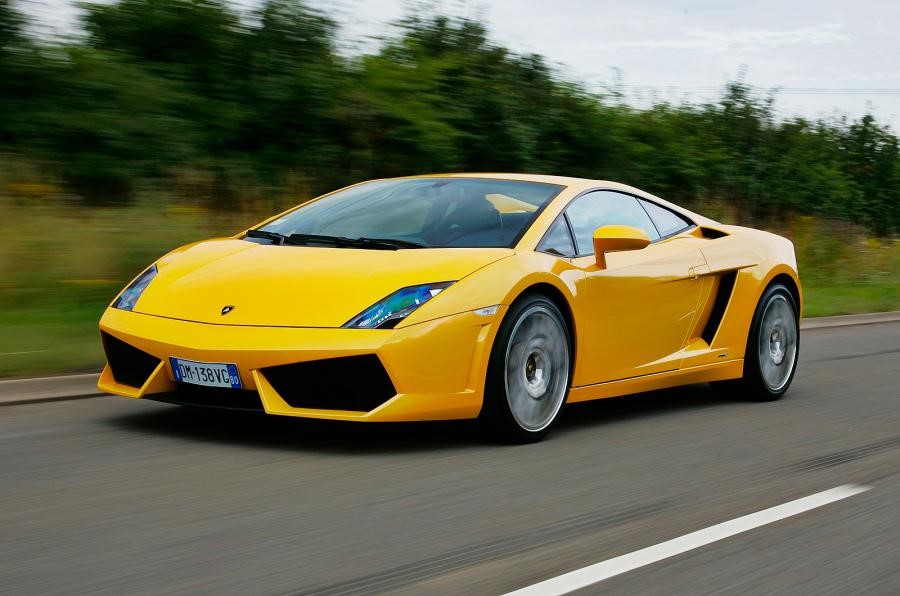
Gallardo
Production 2003–2013
Model years 2004–2014
Assembly Italy: Sant’Agata Bolognese
Designer
Italdesign Giugiaro (initial design)
Luc Donckerwolke (final design)
Walter de Silva (mid-cycle refresh)
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Body style 2-door coupé
2-door convertible (Spyder)
Layout
Longitudinal, mid-engine, all-wheel-drive (LP560-4 & LP570-4)
Rear mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive (LP550-2)
Related
Audi R8 (Type 42)
Lamborghini Sesto Elemento
Lamborghini Egoista
Powertrain
Engine
5.0 L even firing V10 (1st Generation)
5.2 L odd firing V10 (2nd Generation)
Transmission 6-speed manual
6-speed e-gear electrohydraulic manual
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,560 mm (101 in)
Length 4,300–4,386 mm (169–173 in)
Width 1,900 mm (75 in)
Reventon
Manufacturer Lamborghini
Production 2007-2009
21 produced (1 for museum)
Assembly Italy: Sant’Agata Bolognese
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Body style 2-door coupé
Layout Mid-engine, all wheel drive
Doors Scissor
Related Lamborghini Murciélago LP640
Powertrain
Engine 6.5 L V12
Transmission 6-speed e-gear semi-automatic
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,665 mm (104.9 in)
Length 4,700 mm (190 in)
Width 2,058 mm (81.0 in)
Height 1,135 mm (44.7 in)
Curb weight 1,665 kg (3,671 lb)

Aventador
Production
February 2011–2017 (LP700-4, LP750-4 SV coupe and roadster)
2017–present (Aventador S, Aventador SVJ)
Assembly Italy: Sant’Agata Bolognese
Designer
Filippo Perini (original design)
Mitja Borkert (Aventador S)[1]
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Body style
2-door coupé
2-door roadster
Layout Mid-engine, all-wheel drive
Doors Scissor
Related Lamborghini Veneno
Lamborghini Centenarió
Powertrain
Engine 6.5 L L539 V12
Power output
515 kW (700 PS; 690 hp) (Aventador)
545 kW (740 PS; 730 hp) (Aventador S)
550 kW (750 PS; 740 hp) (Aventador SV)
565 kW (770 PS; 760 hp) (Aventador SVJ)
Transmission 7-speed ISR semi-automatic
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,700 mm (106.30 in)
Length 4,780 mm (188.19 in)
Width 2,030 mm (79.92 in) (with mirrors: 2,265 mm (89.17 in))[2]
Height 1,136 mm (44.72 in)
Curb weight
1,575 kg (3,472 lb) (dry) LP700-4, LP740-4 S[1]
1,731 kg (3,816 lb) (with fluids, Eur)[3]
1,853 kg (4,085 lb) (with fluids, US)[4]
1,769 kg (3,900 lb) LP 750-4 SV (with fluids, US)[5]
1,819 kg (4,010 lb) LP 750-4 SV Roadster (with fluids, US)
1,525 kg (3,362 lb) LP 750-4, LP 770-4 SVJ (dry)
Centenerion
Production
2016–2017
(20 coupés and 20 roadsters) [1]
Assembly Italy: Sant’Agata Bolognese
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Body style
2-door coupé
2-door roadster
Layout Mid-engine, all-wheel-drive
Doors Scissor
Related Lamborghini Aventador
Powertrain
Engine 6.5 L L539 V12
Transmission 7-speed ISR semi-automatic
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,700 mm (106.3 in)
Length 4,924 mm (193.9 in)
Width 2,062 mm (81.2 in)
Height 1,143 mm (45.0 in)
Curb weight
Coupé: 1,520 kg (3,351 lb) (dry)
1,764 kg (3,889 lb) (with fluids)
Roadster: 1,570 kg (3,461 lb) (dry)
1,814 kg (3,999 lb) (with fluids)
Sesto elemento
Manufacturer Lamborghini
Production 2011–2012 (20 produced)
Assembly Italy: Sant’Agata Bolognese
Designer Filippo Perini
Body and chassis
Class Track day car
Body style 2-door coupé
Layout Mid-engine, all-wheel-drive
Related Audi R8
Lamborghini Gallardo
Powertrain
Engine Odd-firing 5.2 L Lamborghini V10
Transmission 6-speed e-gear automated manual
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,560 mm (101 in)
Curb weight 999 kg (2,202 lb)

Huracan
Power (at rpm)
449 kW (602 hp; 610 PS) at 8,250 rpm
Torque (at rpm)
560 N⋅m (413 lb⋅ft) at 6,500 rpm
Power to weight ratio
(without fluids)
2.36 kg (5.20 lb) / hp
0 to 100 km/h (62 mph) (seconds)
3.2
2.5 (C&D)
Top speed
>325 km/h (202 mph)
342 km/h (213 mph)
Braking 100 km/h-0
31.9 metres
43.9m (R&T)
AVENTADOR S
Model: Lamborghini Aventador
Number of cylinders: 12
Horsepower: 544 kW
Engine: 6.5 L V12
Payload: 525 kg
Curb weight: 1,575 kg
Torque: 690 N·m
Dimensions: 4,780 mm L x 2,030 mm W x 1,136 mm H
VENONO
Production 2013–2014
(5 coupés, 9 roadsters)
Assembly Italy: Sant’Agata Bolognese
Designer
Filippo Perini
Body and chassis
Class Sports car (S)
Body style
2-door coupé
2-door roadster
Layout Mid-engine, all-wheel-drive
Doors Scissor
Related Lamborghini Aventador
Powertrain
Engine 6.5 L L539 V12
Transmission 7-speed ISR semi-automatic
Dimensions
Wheelbase 2,700 mm (106.3 in)
Length 5,020 mm (197.6 in)
Width 2,075 mm (81.7 in)
Height 1,165 mm (45.9 in) Curb weight 1,490 kg (3,285 lb) (Roadster; dry) 1,450 kg (3,197 lb) (Coupe; dry)

SVJ
ENGINE.
TYPEV12, 60°, MPI
DISPLACEMENT 6498 cc
BORE X STROKE Ø 95 mm x 76,4 mm
COMPRESSION RATIO 11.8 ± 0.2
MAX. POWER566 kW (770 CV) at 8.500 rpm
MAX. TORQUE720 Nm at 6.750 rpm
WEIGHT-TO-POWER RATIO 1,98 kg/CV
LUBRICATIONDry sump
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM EURO 6 – LEV 3
TRANSMISSION
TRANSMISSION TYPE4WD with Haldex generation IV
GEARBOX7 speed ISR, shifting characteristic depending on drive select mode
URUS
Production February 2018–present
Model years 2018–present
Assembly Italy: Sant’Agata Bolognese
Designer
Filippo Perini (concept)
Mitja Borkert (production version)[1]
Body and chassis
Class Mid-size luxury crossover SUV
Body style 5-door SUV
Layout Front-engine, four-wheel-drive
Platform VW MLBevo
Related
Audi Q7
Audi Q8
Bentley Bentayga
Porsche Cayenne
Volkswagen Touareg
Powertrain
Engine 4.0 L FSI twin-turbocharged V8
Power output 478 kW (641 hp; 650 PS)
Transmission 8-speed ZF 8HP automatic[2]
Dimensions
Wheelbase 3,002 mm (118.2 in)
Length 5,113 mm (201.3 in)
Width 2,017 mm (79.4 in)
Height 1,638 mm (64.5 in)
Curb weight 2,200 kg (4,850 lb)
